Figure 8.
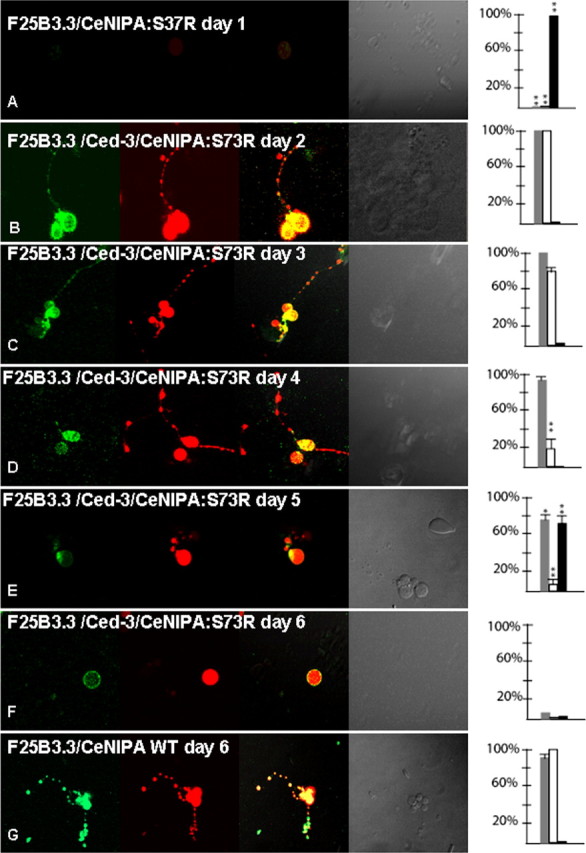
Neurodegeneration of C. elegans neurons expressing mutant forms of CeNIPA. Analysis of primary neuronal C. elegans cultures from double-transgenic animals PF25B3.3::dsRED;CeNIPAS73R::EGFP (A) or PF25B3.3::dsRED;CeNIPAS73R::EGFP;ced-3(n7127) (B–F), in which promoter-generated signal served as a marker of axonal structural integrity. The first column shows EGFP signal by CeNIPA, the second column dsRED signal driven by the F25B3.3 promoter, the third column merge images, the fourth column DIC images, and the fifth plotting of neuronal viability (gray bar shows percentage of viable neurons, white bar percentage of axons with preserved GFP signal, and black bar percentage of neurons undergoing axonal degeneration assessed by the presence of dsRED axonal signal, **p < 0.01). A shows nonviable CeNIPAS73R::EGFP without any differentiation on day 1. Neuronal cultures established from transgenic animals PF25B3.3::dsRED;CeNIPAS73R::EGFP;ced-3(n7127) were viable with a differentiation of neuronal processes and a strong CeNIPAS73R::EGFP signal until day 3 (B, C). The majority of neurons showed signs of reduced EGFP signal between days 3–4 but without signs of axonal structural disintegration as judged by dsRED signal (D). Cultured neurons underwent axonal degeneration (E) followed by neuronal death (F) with the majority of neurons losing viability on days 6 and 7. G shows an example of PF25B3.3::dsRED;CeNIPAWT::EGFP;ced-3(n7127) expressing a WT CeNIPA protein on day 6 with well differentiated axonal processes and strong presence of CeNIPA::EGFP-positive structures in axons. T144R mutations had essentially identical effect on survival and differentiation of neurons (data not shown).
