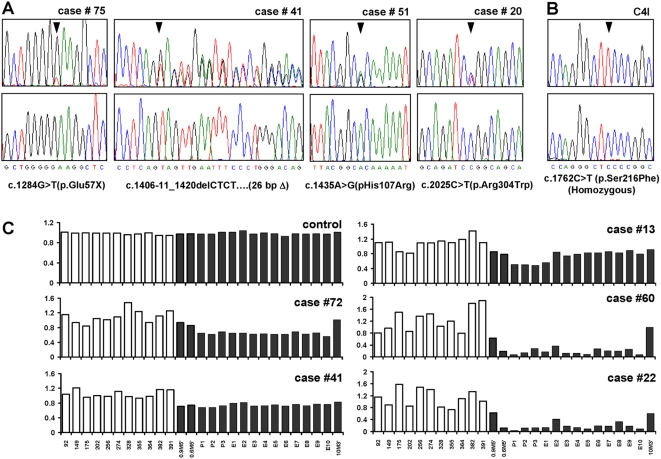
Figure 1. Somatic mutations and deletions of LKB1 in cervical tumors.
(A) Representative chromatograms of primary tumors. (B) C4I cell line. Lower panels, control DNA samples from each patient (for C4I, human peripheral leukocyte DNA). Wild-type sequences are shown below. Chromatograms represent forward strand except case #41 where reverse complement is shown to more clearly illustrate the deletion. Mutations are heterozygous except where indicated. (C) LKB1 deletions in primary cervical tumors by MLPA. Bars = relative signal intensity per probe. Sixteen probes (black) correspond to LKB1 locus on chromosome 19. Probe identifiers shown below. Probes 0.9M5′ and 0.6M5′ are ∼900 and 600 kb 5′ of locus (telomeric), while 10M3′ is ∼10000 kb 3′ (centromeric); remaining 13 probes correspond to LKB1 noncoding/coding exons. White bars correspond to randomly selected probes from other chromosomes.