Figure 1.
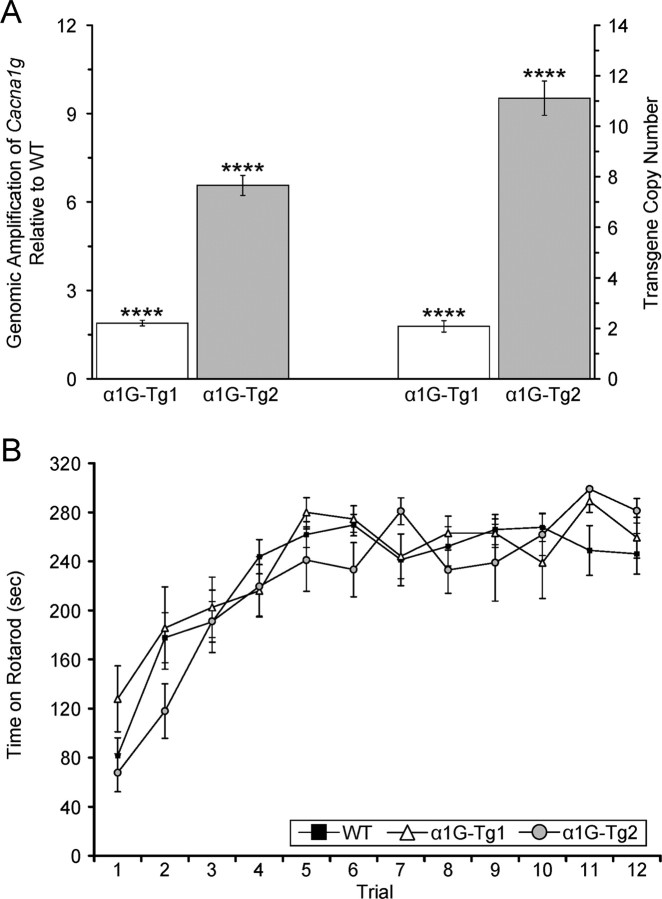
Variable transgene integrations generate low and high copy number transgenic mice without overt neurological defects. A, Quantitative PCR assay comparing amplification from transgenic and WT genomic DNA detecting the Cacna1g target gene and the Scn5a normalizer gene. The α1G-Tg1 line bears an estimated 1–2 transgene integrations (n = 12), and the α1G-Tg2 line bears an estimated >10 copies (n = 24). The transgene copy number is calculated as 2 × (expression fold change) − 2, as described in Materials and Methods. Quantitative data represent mean ± SEM. ****p < 0.001 versus WT controls. B, WT (n = 16), α1G-Tg1 (n = 10), and α1G-Tg2 (n = 9) mice were tested for motor coordination using an accelerating rotarod assay for three consecutive days with four trials/d. The tests revealed no significant differences in time on the rotarod between each transgenic line and WT controls, as each genotype performed similarly for each trial. Quantitative data represent mean ± SEM; p > 0.05 versus WT controls.