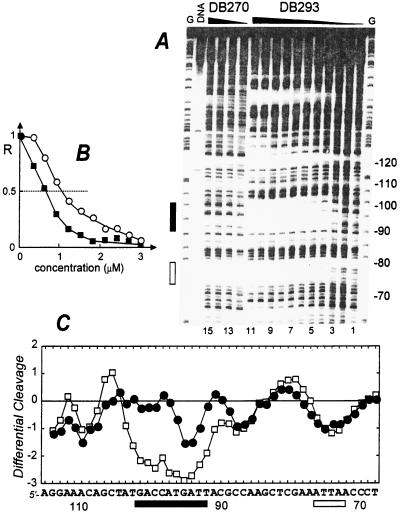
Figure 2.
Quantitative DNase I footprinting titration experiment with DB293 on the 265-bp DNA fragment. The EcoRI-PvuII restriction fragment from plasmid pBS was 3′-end-labeled at the EcoRI site with [α-32P]dATP in the presence of AMV reverse transcriptase. (A) The products of the DNase I digestion were resolved on an 8% polyacrylamide gel containing 8M urea. Drug concentrations are (lanes 1–11) 0, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2, 1.5, 1.8, 2.1, 2.4, 2.7, and 3.0 μM for DB293 and (lanes 12–15) 0, 1, 2, and 5 μM for DB270. Tracks labeled G represent dimethyl sulfate-piperidine markers specific for guanines. The track labeled DNA contained no drug and no enzyme. Numbers at the right side of the gel refer to the numbering scheme of the fragment. The rectangles on the right side refer to the positions of an AT-rich (open box) and a GC-rich (filled box) binding site for DB293. (B) Footprinting plots for the binding of DB293 to the AT site 5′-AATTAA (open circles) and the GC-rich site 5′-ACCATG (filled squares). The relative band intensity R corresponds to the ratio Ic/Io, where Ic is the intensity of the band at the ligand concentration c and Io is the intensity of the same band in the absence of DB293. The differential cleavage plots in C compare the susceptibility of the DNA to cutting by DNase I in the presence of 5 μM DB270 (filled circles) or 1.5 μM DB293 (open squares). Deviation of points toward the lettered sequence (negative values) corresponds to a ligand-protected site and deviation away (positive values) represents enhanced cleavage. The vertical scale is in units of ln(fa) − ln(fc), where fa is the fractional cleavage at any bond in the presence of the drug and fc is the fractional cleavage of the same bond in the control. The results are displayed on a logarithmic scale for the sake of convenience. The rectangles below the sequence show the positions of the AT binding site (open box) and the GC-rich site (filled box). Footprinting reactions, separation of cleavage products, and data analysis were carried out as described (10).