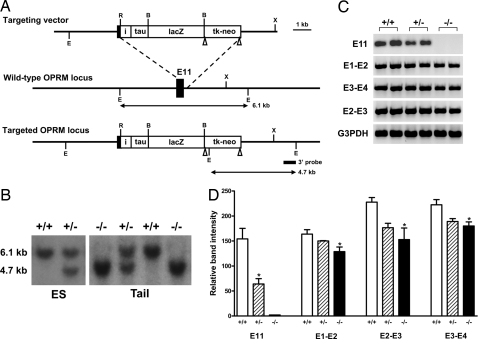
Fig. 2.
Gene targeting exon 11 in the OPRM gene. (A) Schematic of the targeting strategy. The exon 11 coding region and its adjacent intron region are replaced with the IRES/τ/LacZ/loxP-pgk/neo-loxP cassette in 129/SV ES cells through homologous recombination with the targeting vector. Exon 11 is indicated by a black box: i, the internal ribosome entry sequence (IRES); tk, the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene; neo, the neomycin resistance gene. The expected EcoRV-digested fragment lengths for wild-type and targeted alleles are indicated by arrows. 3′ probe is indicated by a short line. Restriction sites: E, EcoRV; R, EcoRI; B, BamHI; X, XbaI. LoxP sites are indicated by triangles. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from ES cells and mouse tail. DNA is cut with EcoRV and hybridized with the 3′ probe. The 6.1 kb upper band represents the wild-type allele and the 4.7 kb lower band is the targeted allele. Genotypes: +/+, wild-type; +/−, heterozygous; and −/−, homozygous. (C) RT-PCR. RT is performed by using SuperScript II reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) with total RNA from mouse brain. The first-strand cDNA is then used as template in PCRs to amplify the corresponding fragments with appropriate primers. (D) Semiquantification of PCR products. The PCR products are analyzed in 1.5% agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide, and photographed with FluorChem 8000 Image system (Alpha Innotech). The relative band intensities from the gel are quantified with AlphaEase FC software and normalized with the intensities from G3PDH bands. Comparisons are made by using ANOVA, which demonstrated a significant difference among the groups (P <0.04) with post hoc Tukey tests confirming that the knockout groups are significantly lower (P <0.05) than wild-type groups, except for E11 where only the wild-type and heterozygous groups are compared by using a Student's t test (P <0.02) because there is no observable product in the knockout animals.