Fig. 1.
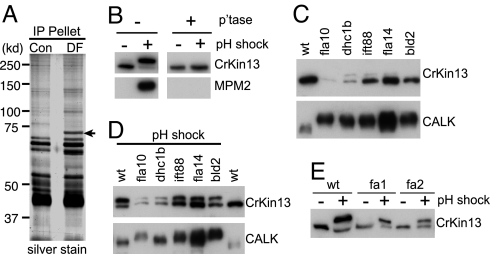
Posttranslational modification of CrKinesin-13 (A) MPM2 antibody immunoprecipitates a 70-kDa protein from pH-shocked cells. Cell lysates from control (con) cells and pH-shocked cells (DF) were incubated with MPM2 antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting (Fig. S1) and silver staining. (B) CrKinesin-13 is phosphorylated during pH shock, and the phosphorylated CrKinesin-13 is the antigen recognized by the MPM2 antibody. Cell lysates from control and deflagellated cells were treated with or without phosphatase followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-CrKinesin-13 and mAb-MPM2. (C) CrKinesin-13 properties in mutants defective in flagellar assembly. The indicated mutant and wild-type (21gr) cells were analyzed by immunoblotting using the CrKinesin-13 antibody. (D) CrKinesin-13 is modified during the pathways activated by pH shock. The flagellar mutants were subjected to pH shock along with wild-type cells, frozen within 1 minute, and subsequently analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunobloting. (E) The fa1 and fa2 mutants, which are defective in flagellar detachment, undergo pH shock-induced modification of CrKinesin-13. Immunoblot analysis of 21gr, fa1, and fa2 mutant cells was carried out before and after pH shock.