Fig. 4.
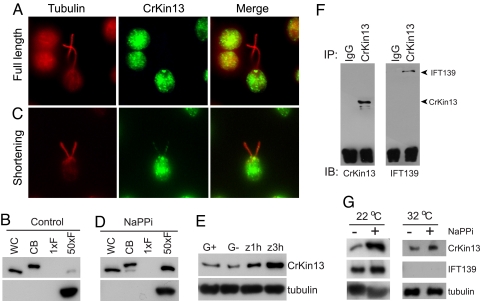
Transport of CrKinesin-13 into flagella is triggered when the flagellar shortening pathway is activated and transport requires IFT. (A) Immunofluorescence of control cells under standard culture conditions. Staining with anti-CrKinesin-13 was detected in the basal body region, and little if any was detected in the flagella. (B) Immunoblot of whole cells (WC), cell bodies (CB), and flagella (F) with anti-CrKinesin-13. CrKinesin-13 was predominantly localized to the cell body (note that the pH shock used for deflagellation caused CrKinesin-13 phosphorylation). (1xF: One cell equivalent of flagella; 50xF: 50 cell equivalents of flagella.) Staining with alpha tubulin antibody documented equal loading. (C) Immunofluorescence of cells undergoing flagellar disassembly. CrKinesin-13 staining was detected along the length of the flagella and at the tip. (D) CrKinesin-13 in the flagella increased within 5 minutes after cells were placed in NaPPi. (E) Immunoblots of flagella from gametes and the zygotes that formed at 1 hour and 3 hours after gametes were mixed. CrKinesin-13 in the flagella increased during zygotic flagellar disassembly. G+, mt+ gametes; G−, mt− gametes; Z, zygotes. Alpha tubulin was used as loading control. (F) Co-immunoprecipitation of CrKinesin-13 and IFT particles. The flagellar membrane/matrix fractions of flagella isolated 5 minutes after transfer of cells to NaPPi were used for immunoprecipitation with anti-CrKinesin-13 or preimmune IgG. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed with anti-CrKinesin-13 and anti-IFT139 antibodies. (G) Failure of CrKinesin-13 to be transported into flagella in the fla10–1 mutant at the non-permissive temperature after induction of flagellar disassembly by NaPPi. fla10–1 Cells were incubated at 22 °C or 32 °C for 1 hour followed by incubation in 20 mM NaPPi for 5 minutes at the same temperatures, and the flagella were isolated and analyzed by immunoblotting. Alpha tubulin was used as a loading control and an anti-IFT139 antibody was used to detect IFT particles.