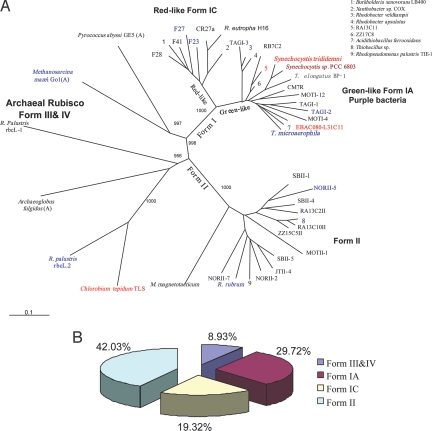
Fig. 2.
Rubisco genes detected in the samples. (A) Phylogenetic tree based on the RubisCO large-subunit amino acid sequences obtained by GeoChip hybridization. Tree topography and evolutionary distance are given by a neighbor-joining method with Kimura distances. This tree is unrooted, with 1,000 replicates of bootstrapping. Bootstrap values are indicated only at major nodes of the tree. The designation of different colors is as follows: Red indicates unique sequences in Proto-I (4 genes), and dark red signifies the single sequence discovered in both Proto-I and 4143-1; blue designates the common sequences from both Proto-O and 4143-1 (10 genes); and black indicates the unique sequences found in 4143-1. All genes detected in Proto-I and Proto-O are listed here, but only the genes with signal intensities greater than 1 from 4143-1 were included in the tree. All genes found in Proto-O could be found in 4143-1. (Scale bar: 0.1 substitutions per site.) (B) Percentage of different types of rbcL genes detected in 4143-1.