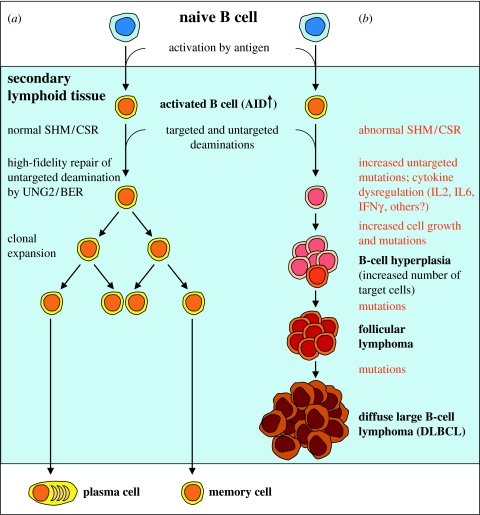
Figure 1.
Model of B-cell lymphoma development in Ung-deficient mice. (a) The pathway illustrates the normal development of Ung+/+ B cells after translocation to secondary lymphoid tissues, leading to antibody-secreting plasma cells and memory cells. (b) The pathway models how cytokine dysregulation and increased accumulation of untargeted mutations in Ung−/− B cells result in lymphoid hyperplasia and increased number of cells having a mutator phenotype. Eventually, this may lead to the development of follicular lymphoma and progression to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.