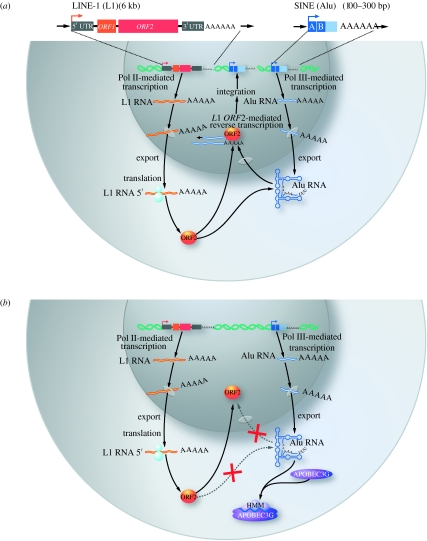
Figure 4.
HMM A3G restricts Alu retrotransposition. (a) Alu retrotransposition mediated by long interspersed nuclear elements-1 (L1). Functional L1 elements are 6-kb-long autonomous retroelements that contain an internal RNA polymerase II (Pol II) promoter within their 5′-UTR, two open reading frames (ORF1 and ORF2), and a 3′-UTR. SINEs, including the most prominent and active member, Alu, are short RNA polymerase III (Pol III)-transcribed retroelements that contain an internal promoter but no protein coding capacity. Successful retrotransposition of Alu elements depends on their ability ‘to steal’ the reverse transcriptase/endonuclease enzymes encoded by L1 ORF2. (b) Non-enzymatic inhibitory mechanism for A3G to restrict Alu. Human A3G impairs the retrotransposition of Alu by sequestering Alu RNA transcripts in the cytoplasmic HMM complexes, especially Staufen-containing RNA granules, away from the nuclear L1 machinery, thereby interdicting the retrotransposition cycle.