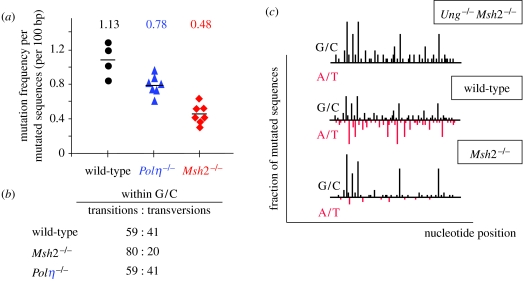
Figure 1.
Profound alteration of the mutation profile of MSH2-deficient B cells. (a) A two- to three-fold reduction in hypermutation in MSH2-deficient B cells. Mutation frequency of JH4 intronic sequences from Peyer's patch PNAhigh B cells was determined for individual mice. (b) A bias for G/C transitions in JH4 sequences from Peyer's patch B cells in MSH2-deficient animals. (c) A schematic of the distribution of mutations along the JH4 intronic sequence of Peyer's patch PNAhigh B cells, with G/C mutations plotted above the line representing the JH4 sequence and A/T mutations below. This conceptual representation illustrates the similar quantitative levels of G/C mutagenesis at hotspot positions between the Msh2×Ung−/− and the Msh2−/− backgrounds, while being greatly diminished at other G/C bases. G/C mutagenesis is overall lower in the wild-type context, in which approximately half of the deaminated cytosines are repaired to generate mutations at A/T bases. Mutation data taken from Rada et al. (2004) and Delbos et al. (2007).