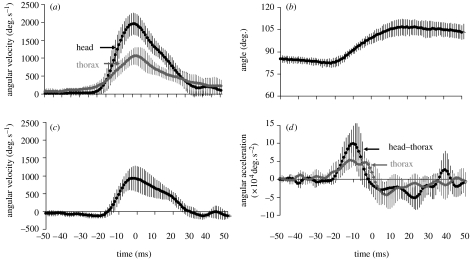
Figure 3.
Head turn kinematics in C. dalmanni. The curves are averages (±1 s.d.) from five turns with the same head turn size=60°. The curves were averaged in a 100 ms time window centred (t=0) at the point of maximum angular velocity of the head relative to the surrounding environment. (a) The angular velocity at which the head and thorax are rotated relative to the surrounding background during the turn. (b) The change in the angle between the transverse axis of the head and the longitudinal axis of the thorax. (c) The angular velocity of the head rotation relative to the thorax, i.e. saccade angular velocity. (d) The angular acceleration of the thorax and the angular acceleration of the head relative to the thorax. Note that the turns shown are large relative to the mean turn size observed (table 1). The purpose here is to illustrate the rotational dynamics within a single turn.