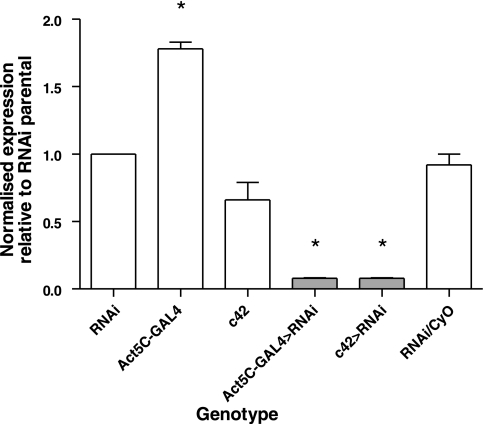
Fig. 6.
Quantification of CG2196-RNA interference (RNAi) induced knockdown of CG2196 mRNA levels. UAS-CG2196-RNAi flies were crossed with a ubiquitous (Act5C-GAL4) and Malpighian tubule principal cell-specific (c42) GAL4 driver and tubule mRNA levels measured by qPCR relative to the rp49 reference gene for both parentals and progeny. Although Act5C-GAL4 flies have expression levels rather higher, and c42 slightly lower, than the RNAi parents, both drive RNAi highly efficiently: CG2196 expression in Act5C-GAL4>progeny is 19× less, and in c42-GAL4>RNAi progeny is 18× less, than in RNAi flies. RNAi/CyO control progeny express CG2196 at levels almost exactly the same as the RNAi flies. Data are expressed relatively to the CG2196 expression of the CG2196-RNAi parental line and normalized against the rp49 reference gene. *Significant change from control (the CG2196-RNAi parental line) (Student's t-test, taking P < 0.05 as significant).