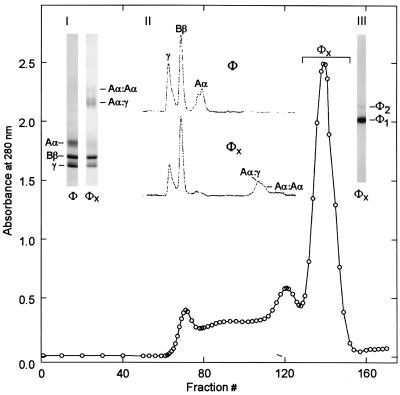
Figure 1.
Isolation of a predominantly intramolecularly crosslinked form of fibrinogen, after its reaction with red cell transglutaminase. (Main graph) Gel filtration of transglutaminase-treated fibrinogen. (Inset I) SDS/PAGE profile for the control fibrinogen (φ), obtained under reducing conditions, was compared with that of the material collected in fractions 129–152, marked φx. (Inset II) Densitometric scans of the gels shown in I. (Inset III) Nonreducing SDS/agarose electrophoresis of the φx pool shows it to be a predominantly monomeric derivative of fibrinogen (φ1), comprising a small percentage of crosslinked dimers (φ2).