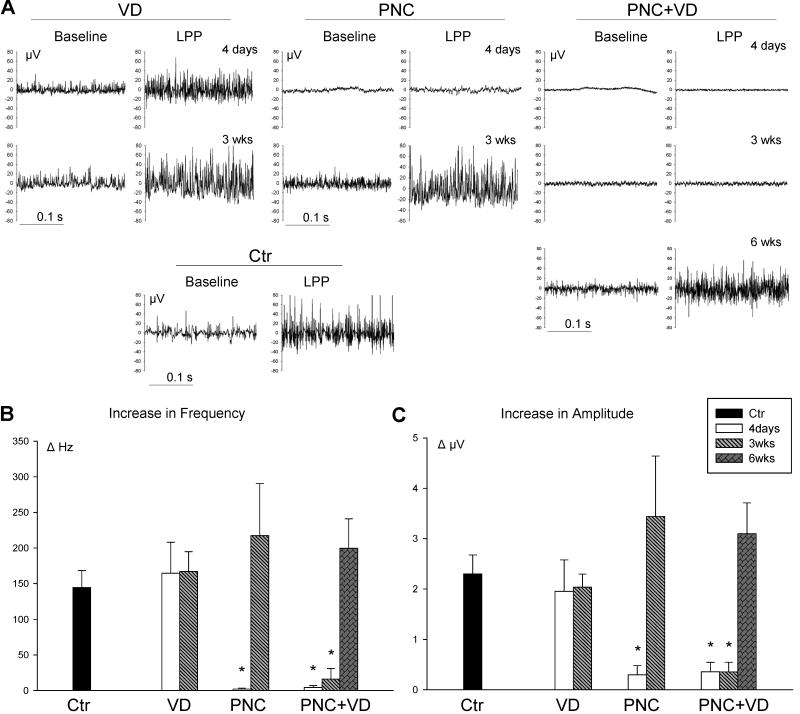
Figure 4.
Pudendal nerve motor branch potential (PNMBP). A. Examples of baseline and peak PNMBP activity during LPP. in control (Ctr) animals, 4 days and 3 weeks (3wks) after vaginal distension (VD) and pudendal nerve crush (PNC), and 4 days, 3 weeks, and 6 weeks (6 wks) after PNC+VD and pudendal nerve transection (PNT). B. Increase in frequency (ΔHz) of PNMBP in response to LPP. C. Increase in amplitude (ΔμV) of PNMBP in response to LPP. Each bar represents mean +/- standard error of the mean of results from 5-13 rats. * indicates a significant difference (P<0.05) compared to control.