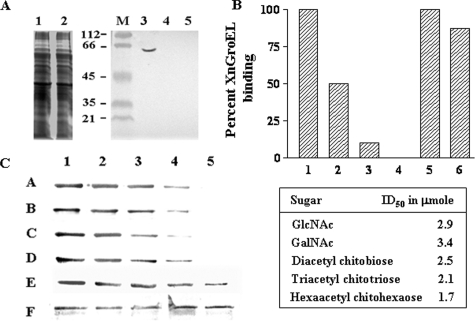
FIGURE 6.
Inhibition of XnGroEL binding to BBMV by different chitin derivatives. A, detection of XnGroEL binding to BBMV after chitinase treatment. The BBMV were incubated with chitinase followed by incubation with XnGroEL, and the membrane proteins were processed and resolved by SDS-PAGE as above. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue; lane 1, untreated BBMV proteins; lane 2, treated with chitinase. Samples in lanes 1 and 2 were blotted with anti-GroEL antibodies after Western transfer; M, prestained markers; lane 3, untreated BBMV; lane 4, BBMV with chitinase and protease inhibitor; lane 5, with chitinase, no protease inhibitor. B, the binding assay mixture contained 20 μg of BBMV, 10 μg of XnGroEL, and the competing compounds. 1, no inhibitory compound; 2, 3, and 4, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.5 mg of solubilized chitin, respectively; 5, 1.0 mg of cellulose; 6, 1.0 mg of chitosan. C, XnGroEL binding in the presence of lanes 1–5, 0, 50, 100, 150, and 200 mm GalNAc, respectively (A); lanes 1–5, 0, 50, 100, 150, and 200 mm GlcNAc, respectively (B), lanes 1–5, 0, 50, 100, 150, and 200 mm diacetyl chitobiose, respectively (C), lanes 1–5, 0, 50, 75, 100, and 125 mm triacetyl chitotriose, respectively (D); lanes 1–5, 0, 20, 40, 60 and 80 mm hexaacetyl chitohexaose, respectively (E); loading control, BBM blotted with antibody against N-aminopeptidase (F). The table shows ID50 values calculated by plotting the integrated density values of the bands shown in panel C. The experiments were repeated three times, and data from one of the representative experiments are presented.