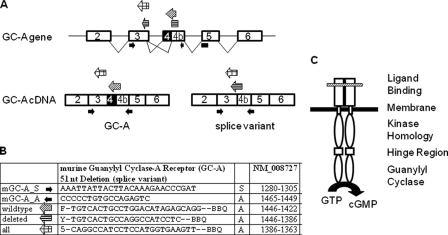
FIGURE 1.
Schemes illustrating relevant parts of the structure of the GC-A gene and cDNA as well as of the GC-A protein. A, structure and alternative splicing of GC-A. The exon-intron organization is shown on the top, including the splicing pattern. The positions of oligonucleotide primers and probes used for quantitative, real time RT-PCR are indicated. Their sequences and the respective nucleotide positions are shown in the table (B). C, the active GC-A receptor is formed by a homodimer and consists of an extracellular (ligand binding), a transmembrane, and three intracellular domains. The variant lacks 17 amino acids (ΔLys314–Gln330) in the membrane-distal part of the extracellular domain (marked by a hatched bar).