FIGURE 3.
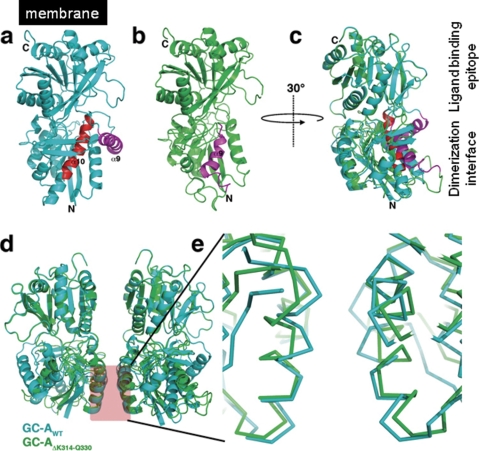
Modeling of the splicing variant GC-AΔLys314-Gln330. a, ribbon representation of the rat GC-A ectodomain with the deletion resulting from the alternative splicing marked in red. Helix α9, which is put into the place of α10 during modeling, is colored in magenta. b, final model of the splicing variant GC-AΔLys314-Gln330 with the new location of helix α9(magenta). c, superposition of the model structures of wild type (cyan) and splicing variant GC-A ectodomain (green). The ectodomain is rotated by 30° in the y axis compared with a and b to show the ligand binding epitope and the dimerization interface at the left-hand side. The overlay shows the structural changes induced by the deletion. d, overlay of the putative receptor dimer upon ANP ligand binding. The receptor dimer assembly was obtained by superposition of the rat GC-A wild type and splice variant onto the ligand-receptor complex of human GC-A (PDB entry 1YK1). e, zoom into the dimerization interface. The splice variant (green) shows significant changes in the α-helix 2 in the dimerization interface that might lead to alteration in the receptor dimer architecture and hence result in loss of ANP binding of the splice variant.