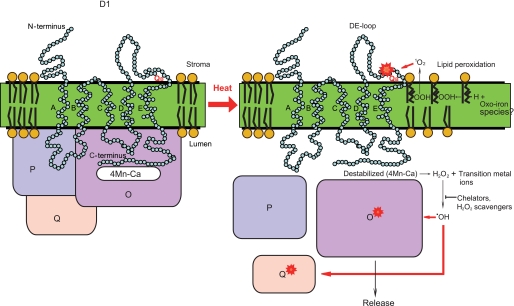
FIGURE 10.
A model for the effects of moderate heat stress on PS II. At the acceptor side of PS II, heat-induced lipid peroxidation produces 1O2, which damages the DE-loop of the D1 protein and causes cleavage as well as aggregation of the D1 protein. At the donor side of PS II, heat induces destabilization of the four manganese-calcium cluster and generates H2O2. The H2O2 then reacts with transition metal ions to produce OH·, which in turn damages proteins, including D1 and D2 and the extrinsic PsbO and Q proteins. The extrinsic proteins are probably released from PS II after damage takes place in the D1 protein.