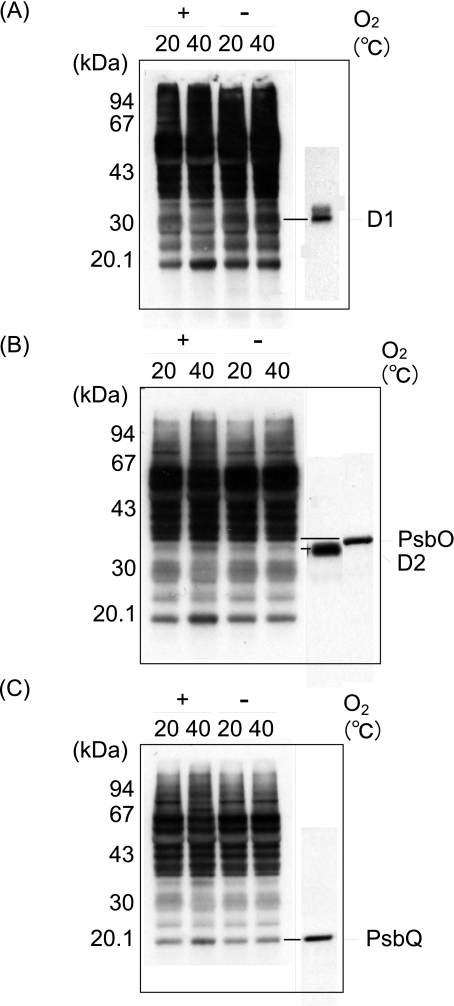
FIGURE 2.
Detection of oxidation of the proteins in the thylakoid membranes induced by moderate heat stress. Thylakoid membranes were heat-treated at 40 °C for 30 min under aerobic (+O2) and anaerobic (-O2) conditions, and the content of protein carbonyl was measured by an Oxi-Blot protein oxidation detection kit. The control temperature is 20 °C. A, fluorograms of Oxi-Blot (left) and of Western blot analysis with the antibody against the DE-loop of the D1 protein (right). B, fluorograms of Oxi-Blot (left) and of Western blot analysis with the antibody against the D2 and PsbO proteins (right). C, fluorograms of Oxi-Blot (left) and of Western blot analysis with the antibody against PsbQ. A–C, the same PVDF membranes with the thylakoid proteins blotted were exposed to x-ray films for different periods to clarify the differences in the degree of protein oxidation between the aerobic and anaerobic conditions, as well as between the stress temperature and the control conditions.