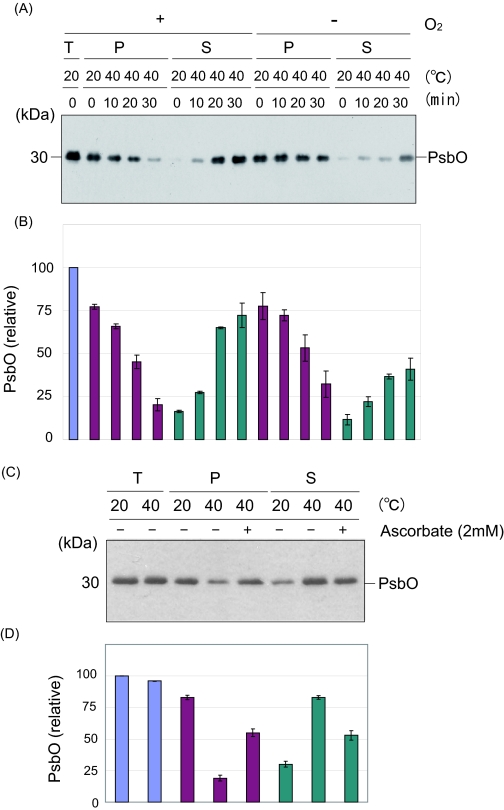
FIGURE 7.
Heat-induced release of the PsbO protein from PS II under the aerobic and anaerobic conditions and the effects of addition of sodium ascorbate on the protein release. A, heat-induced release of the PsbO protein from the PS II membranes under the aerobic (left) and anaerobic (right) conditions. The samples were incubated at 40 °C for the periods indicated. T, P, and S represent the total PS II membranes, the precipitate, and the supernatant of centrifugation after heat treatment of the PS II membranes, respectively. The positions of PsbO and molecular markers are shown on the right and left side of the gel, respectively. B, estimation of the amounts of PsbO in each fraction shown in A. The data are the average of three independent measurements ± S.D. The blue, purple, and cyan bars represent the amount of PsbO protein in the total PS II membranes, the precipitate, and the supernatant of centrifugation after heat treatment of the PS II membranes. C, effects of sodium ascorbate (2 mm) on the release of the PsbO protein from the PS II membranes under heat stress at 40 °C for 30 min. Sodium ascorbate was added prior to the heat treatment where indicated. D, estimation of the amounts of PsbO in each fraction shown in C. The data are the average of three independent measurements ± S.D. The colors of the bars represent the same as those in B.