Figure 1.
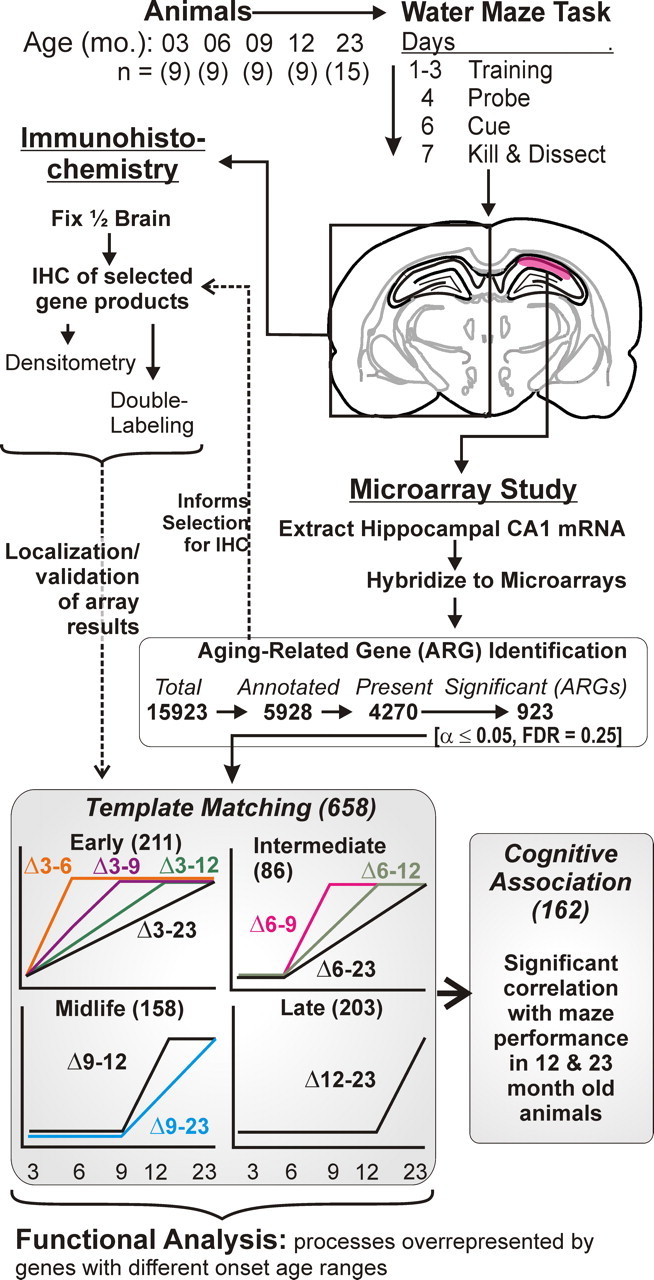
Overview of experimental protocol and microarray analysis procedure. Top, Animals (N = 9–15) from five age groups (3–23 months) were tested on the Morris water maze. Top middle, Brains were removed and one hemisphere was used for immunohistochemistry, and the hippocampal CA1 region (red) of the other hemisphere was subdissected and used for microarray studies. Bottom middle, For microarray analyses, genes were filtered to exclude ESTs and absence calls. The remaining genes/probe sets were tested across age groups by one-way ANOVA. Genes significant by this procedure were designated ARGs. Dashed arrow from ARG identification to selected IHC analyses: ARG identification was used to inform selection for immunohistochemical analysis. Bottom, Based on highest correlation with 1 of 10 idealized templates, ARGs were assigned to one of four basic ages of onset (see Materials and Methods). Note that only upregulated templates were used; downregulated ARGs within each template were identified based on negative, rather than positive, correlations (see Materials and Methods). Templates were then grouped according to onset age ranges (early, intermediate, midlife, and late) determined from the age point at which the initial deflection in expression from the 3 month group was detected. For all ARGs assigned an onset range, correlation of gene expression and MWM performance in the 12- and 23-month-old animals was tested (Pearson's test). Functional process overrepresentation analysis was performed for ARGs in each onset age range using EASE/DAVID analysis procedures interrogating the Gene Ontology (see Materials and Methods).
