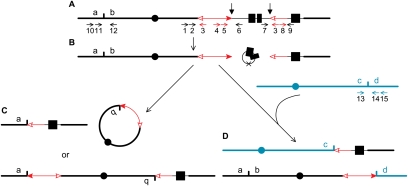
Figure 1.
Model for generation of major chromosome rearrangements by reversed Ac ends transposition. The lines depict maize chromosomes, with centromeres indicated by black and green circles. The red arrows indicate Ac (double-headed arrow) and fAc, a ∼2.0-kb fragment containing the 3′ end of Ac (single arrowhead). The open and solid arrowheads indicate the 3′ and 5′ ends, respectively, of Ac/fAc. The fAc element is inserted into the second intron of the maize p1 gene, whose exons are indicated by solid boxes. The small vertical arrows indicate the Ac transposase cleavage sites. (A) Ac transposase cleaves at the 5′ end of Ac and the 3′ end of fAc. (B) Following transposase cleavage at the junctions of Ac/p1 and fAc/p1, the internal p1 genomic sequences are joined to form a circle. The “×” on the circle indicates the site where joining occurred, marked by a transposon footprint. The Ac 5′ and fAc 3′ ends are competent for insertion anywhere in the genome. C and D depict the outcomes of insertion into two possible target sites (short vertical lines). (C) The Ac/fAc termini insert into a site on the opposite arm of the same sister chromatid; in the top figure, the Ac 5′ end joins to the proximal side of the target site to form a ring chromosome, and the fAc 3′ end joins to the distal side of the target site to form an acentric fragment. (Bottom) Alternatively, ligation of the Ac 5′ end to the distal side of the target site and the fAc 3′ end to the proximal side of the target site would generate a pericentric inversion. (D) The transposon ends insert into a site in another chromosome; the Ac 5′ end joins to the distal side of the target site, and the fAc 3′ end joins to the proximal side of the target site to generate a reciprocal translocation. The short, horizontal arrows indicate the orientations and approximate positions of PCR primers. Primers are identified by numbers above or below the arrows. The structures of P1-rr11 and P1-rr910 are similar to that of the p1 allele in 1A; i.e., the Ac element is located upstream of the p1 gene; in P1-ovov454, however, the Ac element is inserted in intron 2 of p1. Primers 1, 2, and 6 differ for alleles P1-rr11, P1-rr910, and P1-ovov454 due to differences in the Ac insertion sites; see the Materials and Methods for details.