Abstract
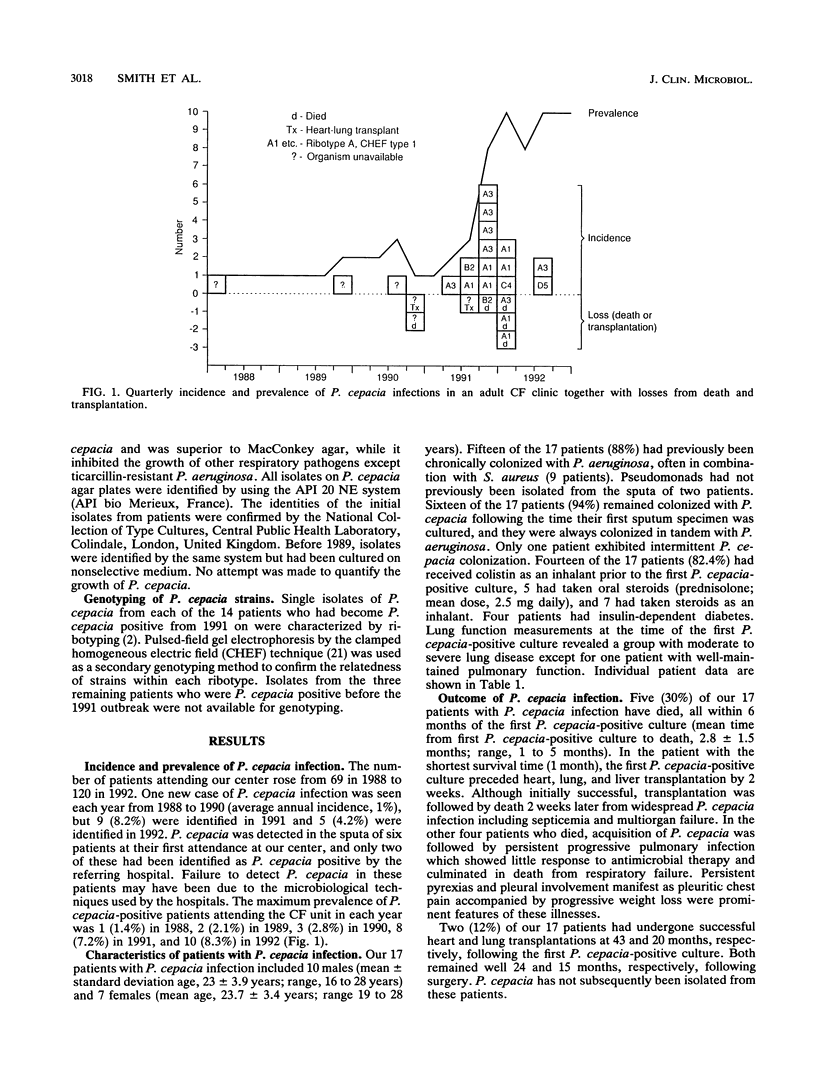
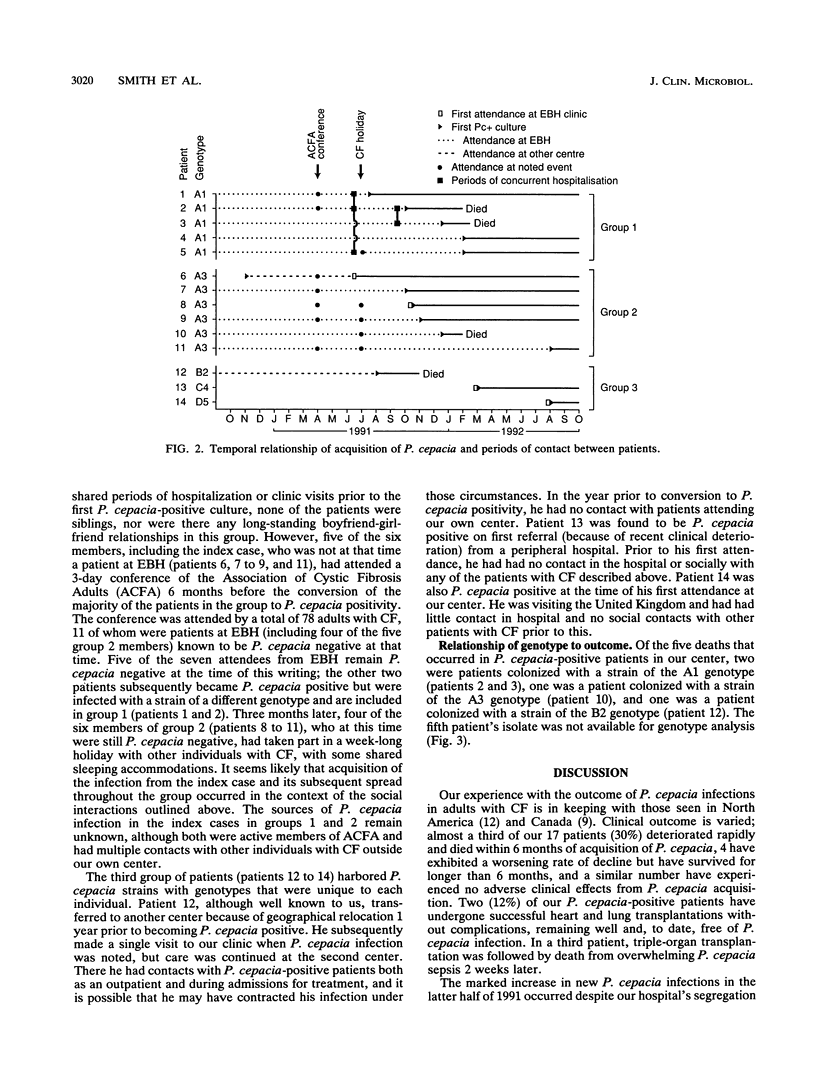
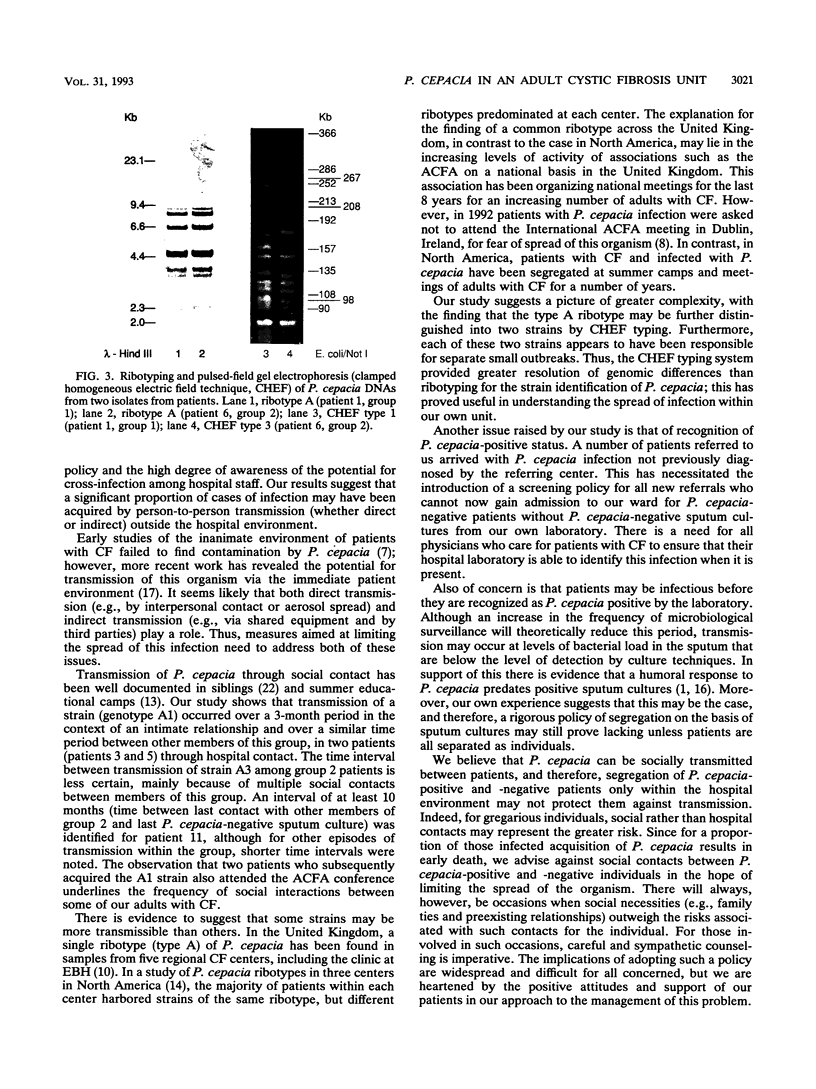
An epidemic of Pseudomonas cepacia occurred in an adult cystic fibrosis center in the United Kingdom, despite a policy of segregation of infected and noninfected patients within the hospital. Investigation of the outbreak by ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to characterize P. cepacia strain genomes together with inquiry into social contacts between patients revealed evidence of person-to-person transmission outside the hospital environment. Segregation policies aimed at reducing the spread of this infection in the cystic fibrosis community need to encompass patient contacts outside the hospital environment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronoff S. C., Quinn F. J., Jr, Stern R. C. Longitudinal serum IgG response to Pseudomonas cepacia surface antigens in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1991;11(4):289–293. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950110404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garaizar J., Kaufmann M. E., Pitt T. L. Comparison of ribotyping with conventional methods for the type identification of Enterobacter cloacae. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1303–1307. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1303-1307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H., Gage P. A., Bradshaw L. M., Schidlow D. V., DeCicco B. T. Isolation medium for the recovery of Pseudomonas cepacia from respiratory secretions of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):5–8. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.5-8.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladman G., Connor P. J., Williams R. F., David T. J. Controlled study of Pseudomonas cepacia and Pseudomonas maltophilia in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Feb;67(2):192–195. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.2.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass S., Govan J. R. Pseudomonas cepacia--fatal pulmonary infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis. J Infect. 1986 Sep;13(2):157–158. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(86)92953-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmann D. A., Klinger J. D. Pseudomonas cepacia: biology, mechanisms of virulence, epidemiology. J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 2):806–812. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80749-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. A., McGowan K. L., Fisher M. C., Schidlow D. V. Pseudomonas cepacia in the hospital setting: lack of transmission between cystic fibrosis patients. J Pediatr. 1986 Jul;109(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80571-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isles A., Maclusky I., Corey M., Gold R., Prober C., Fleming P., Levison H. Pseudomonas cepacia infection in cystic fibrosis: an emerging problem. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80993-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin L. O., Byard P. J., Davis P. B. Effect of Pseudomonas cepacia colonization on survival and pulmonary function of cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990;43(2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(90)90175-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Dasen S. E., Nielson D. W., Stern R. C., Stull T. L. Person-to-person transmission of Pseudomonas cepacia between patients with cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1990 Nov 3;336(8723):1094–1096. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92571-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Mortensen J. E., Dasen S. E., Edlind T. D., Schidlow D. V., Burns J. L., Stull T. L. Ribotype analysis of Pseudomonas cepacia from cystic fibrosis treatment centers. J Pediatr. 1988 Nov;113(5):859–862. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar-Jones L., Paull A., Saunders Z., Goodchild M. C. Transmission of Pseudomonas cepacia among cystic fibrosis patients. Lancet. 1992 Aug 22;340(8817):491–491. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91817-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. W., Doherty C. J., Brown P. H., Greening A. P., Kaufmann M. E., Govan J. R. Pseudomonas cepacia in inpatients with cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1991 Dec 14;338(8781):1525–1525. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92342-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. Pseudomonas cepacia in cystic fibrosis patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Oct;134(4):644–645. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.4.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pseudomonas cepacia--more than a harmless commensal? Lancet. 1992 Jun 6;339(8806):1385–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds E. J., Conway S. P., Ghoneim A. T., Ross H., Littlewood J. M. Pseudomonas cepacia: a new pathogen in patients with cystic fibrosis referred to a large centre in the United Kingdom. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Aug;65(8):874–877. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.8.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Smith E. G., Gumery L. B., Stableforth D. E. Pseudomonas cepacia infection in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1992 Jan 25;339(8787):252–252. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
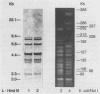
- Struelens M. J., Deplano A., Godard C., Maes N., Serruys E. Epidemiologic typing and delineation of genetic relatedness of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by macrorestriction analysis of genomic DNA by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2599–2605. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2599-2605.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Chorba T. L., Schidlow D. V., White J. W., Hardy K. A., Gilligan P. H., Morgan W. M., Carson L. A., Martone W. J., Jason J. M. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization in patients with cystic fibrosis: risk factors and clinical outcome. J Pediatr. 1985 Sep;107(3):382–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80511-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Martone W. J., Doershuk C. F., Stern R. C., Thomassen M. J., Klinger J. D., White J. W., Carson L. A., Jarvis W. R. Colonization of the respiratory tract with Pseudomonas cepacia in cystic fibrosis. Risk factors and outcomes. Chest. 1987 Apr;91(4):527–532. doi: 10.1378/chest.91.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Doershuk C. F., Stern R. C., Klinger J. D. Pseudomonas cepacia: decrease in colonization in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Oct;134(4):669–671. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.4.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Klinger J. D., Stern R. C. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization among patients with cystic fibrosis. A new opportunist. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 May;131(5):791–796. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.5.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]