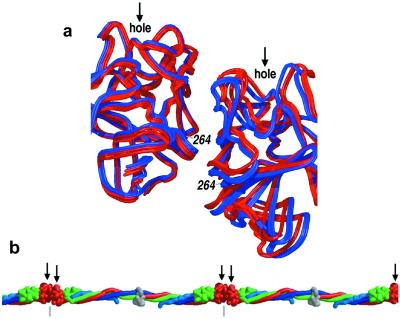
Figure 3.
Conserved end-to-end molecular interactions. (a) Superposition of six γ-domain dimers derived from the various crystals of modified bovine fibrinogen (red) and human fragment D and crosslinked D-dimer (blue) (24, 25) show the γ domains to be similarly “offset” from one another. This feature can be visualized by noting, for example, that γ264 of the right monomer is interacting at the edge of the γ-γ interface whereas in the left monomer it is interacting at the center of the interface. No significant difference in the offset is found among the three bovine γ-domain dimers or among the three human γ-domain dimers (pooled intra-species SD is 0.455 Å). Interspecies amino acid differences at or near the interface (e.g., γ264, which is methionine in human and serine in bovine fibrinogen) probably perturb the docking of the domains, creating a slightly less staggered offset (≈1.7-Å rms difference) in the bovine γ-dimer relative to that in the human dimer. (b) Crystal structure of an end-to-end bonded fibrinogen filament. All γ-domain receptor pockets (shown by arrows) are on the same face of the extended filament.