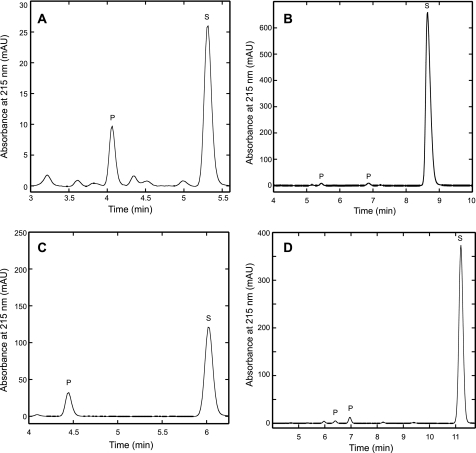
FIGURE 3.
HACN catalyzed the hydration of cis-unsaturated tricarboxylic acids to produce hydroxyacids. Holoenzyme was incubated with cis-homoaconitate analogs for 20 h at 60 °C. The reaction products were separated by reversed phase HPLC with UV absorbance detection in milli-absorbance units (mAU) as described in the text. Substrate peaks (S) were identified by their retention times compared with external standards. Product peaks (P) had absorbance maxima near 205 nm, and they were not observed in control reactions. The unlabeled peaks were also observed in control reactions without enzyme, so they are considered to be contaminants. A, incubation with cis-homoaconitate (S) produced homocitrate (P) that was confirmed by coinjection with (R)-homocitrate. No homoisocitrate was detected in this experiment. B, incubation with cis-homo2aconitate produced two product peaks. C, incubation with cis-homo3aconitate produced a single product peak. D, incubation with cis-homo4aconitate produced two product peaks. The homoaconitate analogs have significantly higher molar absorptivities than their corresponding hydroxy-acids, which preclude direct comparisons of their concentrations by peak area integration.