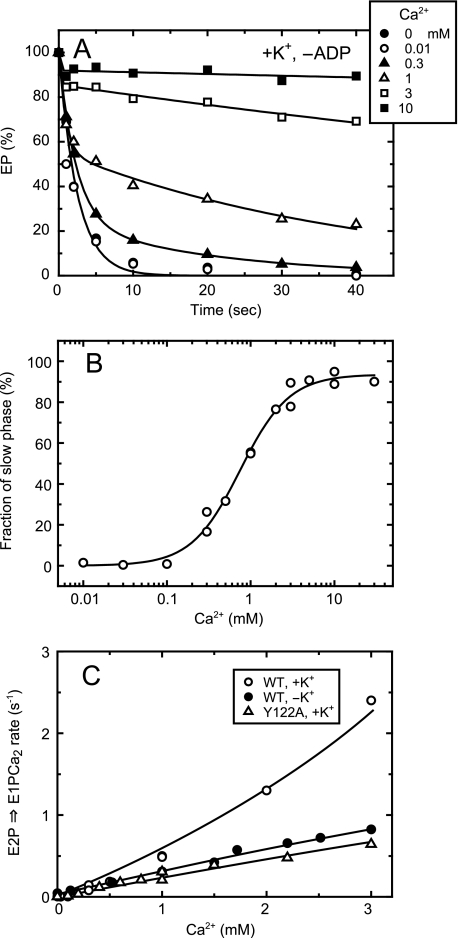
FIGURE 9.
Kinetics of lumenal Ca2+-induced change of E2P to E1PCa2 in the wild type in the presence of K+ without ADP. A, the microsomes expressing the wild type were phosphorylated with 32Pi in the presence of A23187 and absence of Ca2+ and chilled on ice, as described in Fig. 7. Subsequently, the phosphorylated sample was mixed at 0 °C with a 20-fold volume of chase solution containing 105 mm KCl and various concentrations of CaCl2 without ADP, otherwise as described in Fig. 7. The final free Ca2+ concentrations were indicated in the figure. At the indicated time periods after this addition, the chase reaction was terminated by trichloroacetic acid, and the amount of EP was determined. Solid lines show the least squares fit to a double exponential decay. The EP remaining in the second and slow phase was all in the ADP-sensitive form (thus E1PCa2, data not shown), and the first and rapid phase is the forward hydrolysis of E2P without bound Ca2+. B, the fraction of EP in the second phase in the total amount of EP was obtained by extrapolating to the zero time in the double exponential decay fitting, and plotted versus the Ca2+ concentration. The data were fitted well with the Hill equation (solid line), and the Ca2+ concentration giving the 50% saturation and the Hill coefficient were found to be 750 μm and 1.5. Here note that the EP amount in the second phase is dependent on the ratio between the rate of the forward E2P hydrolysis and that of the reverse E2P to E1PCa2 conversion upon the lumenal Ca2+ binding to E2P: the plot reflects the relative values between these forward and reverse rates of E2P rather than the lumenal Ca2+ affinity of E2P. C, by using the data obtained in A and B with the wild type in the presence of K+, the rate of the lumenal Ca2+-induced E1PCa2 formation from E2P (krev (○)) was calculated at each Ca2+ concentration by the equation, krev = khFs/(1 - Fs). Here, Fs is the fraction of EP in the second phase, and kh is the forward hydrolysis rate of E2P without Ca2+. For comparison with the wild type in the absence of K+ (•) and Y122A in the presence of K+ (▵), their lumenal Ca2+ access rates (the rates of the lumenal Ca2+-induced reverse E2P decay via E1PCa2 in the presence of ADP) obtained in Fig. 8A are plotted.