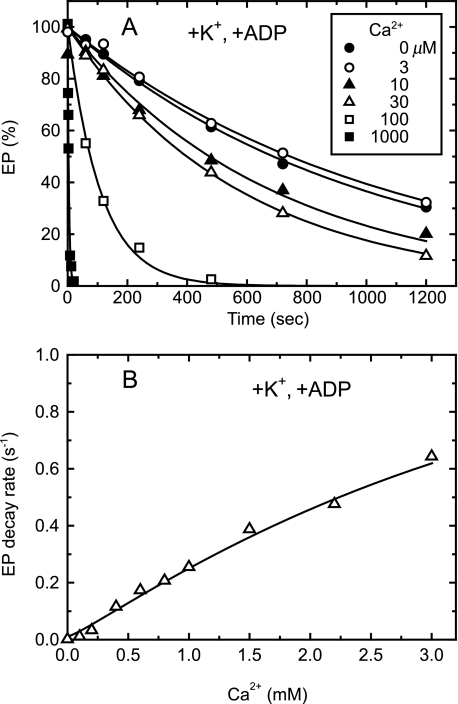
FIGURE 7.
Lumenal Ca2+- and ADP-induced reverse E2P decay of Y122A in the presence of K+. A, microsomes (100 μg/ml) expressing the mutant Y122A were phosphorylated with 32Pi for 10 min at room temperature in the absence of Ca2+ in a medium containing 50 mm MOPS/Tris (pH 7.3), 7 mm MgCl2, 1 mm EGTA, 15 μm A23187, 0.1 mm 32Pi, and 20% Me2SO (that favors extremely the E2P formation (38)), and then the reaction mixture was chilled on ice. Subsequently, the phosphorylated sample was diluted at 0 °C with a 20-fold volume of a chase solution containing 50 mm MOPS/Tris (pH 7.3), 105 mm KCl, 7 mm MgCl2, 1 mm EGTA, 0.1 mm non-radioactive Pi, and 0.105 mm ADP without or with various concentrations of CaCl2 to give the final free Ca2+ concentrations as indicated. At the indicated periods, the chase reaction was terminated by trichloroacetic acid and the amount of EP was determined. Solid lines show the least squares fit to a single exponential decay. The decay rates thus obtained were plotted versus the Ca2+ concentration in panel B.