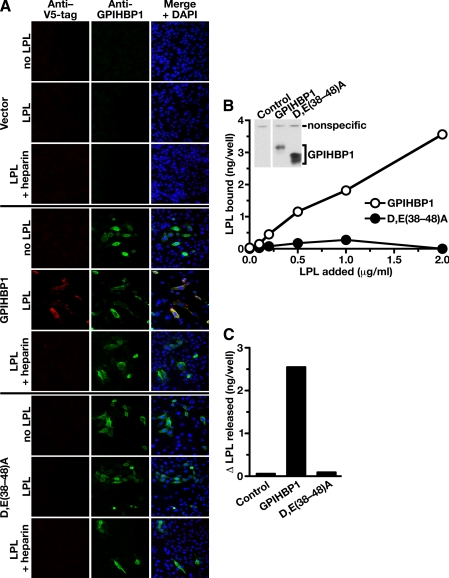
FIGURE 5.
Mutations in the acidic domain of GPIHBP1 prevent the binding of exogenously added LPL. A, binding of a V5-tagged mouse LPL to GPIHBP1-transfected cells. CHO pgsA-745 cells were transiently transfected with wild-type mouse GPIHBP1, the D,E(38-48)A GPIHBP1 mutant, or empty vector. The transfected cells were incubated for 2 h at 4°C with V5-tagged mouse LPL in the presence or absence of heparin (100 units/ml). After washing the cells with ice-cold 1× PBS containing 1 mm MgCl2 and 1 mm CaCl2, the expression of GPIHBP1 and the binding of LPL was assessed by immunofluorescence microscopy with an antibody against GPIHBP1 (green) and an antibody against the V5 tag (red). DAPI (blue) was used to visualize cell nuclei. LPL binding was observed in cells expressing wild-type GPIHBP1 but not in cells that had been transfected with the D,E(38-48)A mutant or empty vector. B, binding of avian LPL to CHO pgsA-745 cells stably transfected with a wild-type GPIHBP1 expression vector or a D,E(38-48)A GPIHBP1 expression vector. After incubating the cells for 2 h with different concentrations of avian LPL, the cells were washed extensively, and the amount of LPL bound to cells was quantified with a sandwich-based ELISA (21). Inset, Western blot showing that both cell lines expressed GPIHBP1. In this experiment, cells from 12-well plates were harvested in 250 μl of lysis buffer, and equal amounts of cell extracts (50 μl) were loaded onto the gel (note the similar intensity of a nonspecific band in all lanes). C, change in the amount of avian LPL in the cell culture medium after PIPLC. Cells that had been stably transfected with wild-type GPIHBP1 or the D,E(38-48)A mutant GPIHBP1 were incubated with avian LPL (0.5 μg/ml). The amount of avian LPL present in the culture medium before and after PIPLC treatment (6 units/ml) for 30 min at 37 °C was quantified by ELISA, and the difference in these values was plotted.