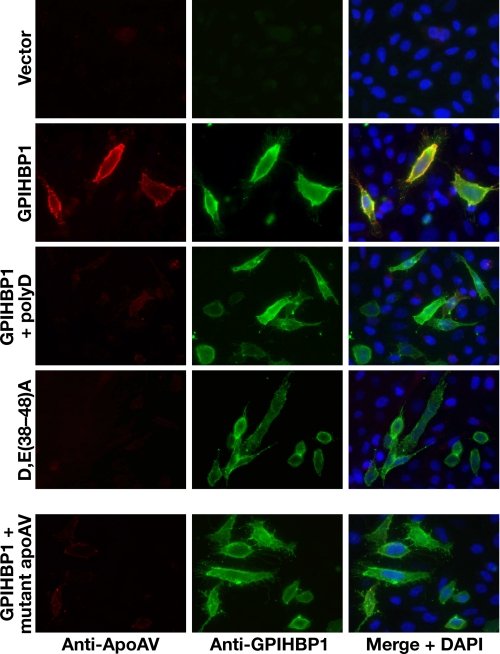
FIGURE 7.
The acidic domain of GPIHBP1 and the heparin-binding domain of apoAV are required for the binding of apoAV to GPIHBP1. CHO pgsA-745 cells were transiently transfected with different GPIHBP1 constructs, and the expression of GPIHBP1 was assessed by immunofluorescence microscopy with an antibody against GPIHBP1 (green); binding of apoAV·DMPC disks to cells was detected with an antibody against apoAV (red). Rows 1-3, immunofluorescence microscopy showing that the binding of apoAV·DMPC disks to cells expressing wild-type GPIHBP1 was eliminated by poly(D) (200 μg/ml). Row 4, immunofluorescence microscopy showing that apoAV·DMPC disks do not bind to cells expressing D,E(38-48)A GPIHBP1. Row 5, immunofluorescence microscopy examining the binding of mutant apoAV·DMPC disks to cells expressing wild-type GPIHBP1. In the mutant apoAV, four of the positively charged residues in the principal heparin-binding domain were replaced with other amino acids (R210E, K211Q, K215Q, K217E).