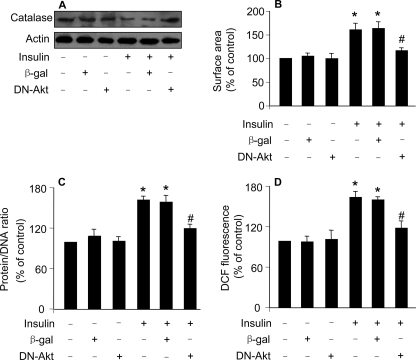
FIGURE 6.
Dominant negative Akt inhibits the decrease of catalase expression and hypertrophy induced by insulin. A, dominant negative Akt (DN-Akt) attenuates the reduction of catalase levels upon treatment with insulin. The neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were infected with Ad-β-galactosidase or Ad-DN-Akt at an m.o.i. of 100. 24 h after infection they were treated with 20 μg/ml insulin. 1 h after treatment cells were collected for the detection of catalase levels by immunoblot. B and C, DN-Akt attenuates hypertrophy upon treatment with insulin. Cardiomyocytes were treated as described for A. 48 h after treatment cells were harvested for the detection of cell surface area (B) or protein/DNA ration (C). *, p < 0.05 versus control; #, p < 0.05 versus insulin alone. D, DN-Akt attenuates ROS elevation induced by insulin. Cardiomyocytes were treated as described for A. 24 h after infection cells were incubated with 5 μm DCF-DA for 30 min at 37 °C, and then treated with 20 μg/ml insulin. ROS was analyzed 1 h after insulin treatment. *, p < 0.05 versus control; #, p < 0.05 versus insulin alone. Data in Fig. 6 are expressed as mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments.