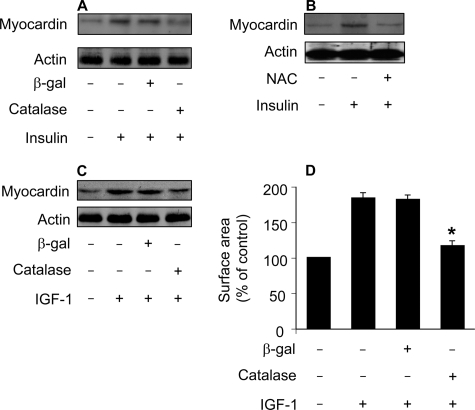
FIGURE 8.
Myocardin up-regulation induced by insulin and IGF-1 can be attenuated by the antioxidant agents. A, catalase is able to attenuate myocardin levels upon treatment with insulin. The neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were infected with Ad-β-galactosidase or Ad-catalase at an m.o.i. of 50. 24 h after infection cells were treated with 20 μg/ml insulin. Cells were harvested for immunoblot analysis of myocardin 1 h after insulin treatment. B, the antioxidant NAC is able to attenuate myocardin levels upon treatment with insulin. Cardiomyocytes were pretreated with 10 mm NAC for 1 h and then treated with 20 μg/ml insulin. Cells were harvested for immunoblot analysis of myocardin 1 h after insulin treatment. C, catalase attenuates myocardin levels upon treatment with IGF-1. Cardiomyocytes were treated as described for A, except that 30 ng/ml IGF-1 was used. D, catalase inhibits hypertrophy upon treatment with IGF-1. Cardiomyocytes were treated as described for C. Cell surface area measurement was performed 48 h after IGF-1 treatment. *, p < 0.05 versus IGF-1 alone. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. A representative blot of three independent experiments is shown in Fig. 8.