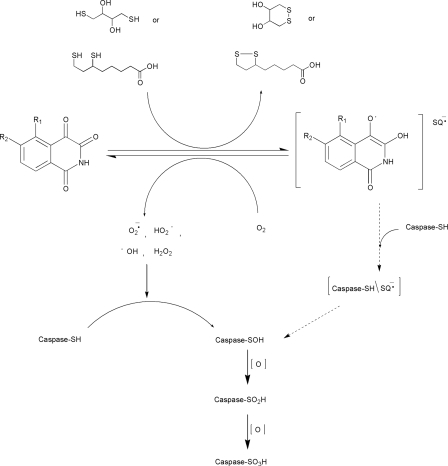
FIGURE 7.
Proposed scheme for the catalytic inactivation of caspase-3 by isoquinoline-1,3,4-trione derivatives through redox cycling. In the presence of DTT in vitro and possibly dihydrolipoic acid in vivo, isoquinoline-1,3,4-trione derivatives rapidly undergo reduction to the corresponding semiquinone anion radicals (RQ-). The reaction is reversible in the presence of atmospheric oxygen by reduction oxygen to ROS. The farther oxidation of DTT and dihydrolipoic acid intermediate also could generate ROS (38, 39). The produced ROS catalyzes the step by step oxidation of the active site cysteine of caspase-3 to the sulfonic acid. The semiquinone anion radicals may also contribute to the specific oxidation of the catalytic cysteine via a intermediate (Caspase-SH/RQ-). Caspase-SH, caspase-SOH, caspase-SO2H, and caspase-SO3H represent the thiol, sulfenic, sulfinic, and sulfonic acid states of the catalytic cysteine.