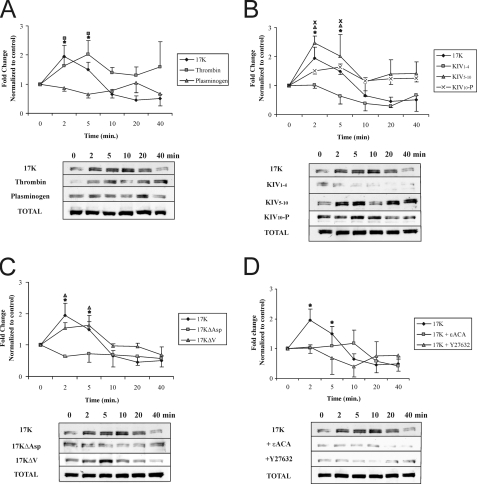
FIGURE 6.
Kringle IV type 10 containing r-apo(a) variants increase MYPT1 phosphorylation in a lysine- and RhoK-dependent manner. HUVECs were serum-starved for 15 min and then treated with 200 nm r-apo(a) variants for the indicated time periods. Total cellular proteins were harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-phospho-MYPT1 (p-MYPT1) and anti-total-MYPT1 (Total-MYPT1). Graphs in each panel show mean band density (normalized to the control) ± S.E. of three independent experiments, and representative Western blots are shown below. The asterisks represent increases in MYPT1 phosphorylation in the presence of 17K r-apo(a) that are significantly different (p < 0.05) from those in the absence of r-apo(a) variants. Other symbols over the plots represent significant differences (p < 0.05) from the normalized control of each r-apo(a) variant represented by the corresponding plot symbols in each panel (as shown in the legends). A, comparison of 17K treatment with TNFα (positive control) and plasminogen (negative control). B, comparison of 17K treatment with deletion mutants (KIV1–4, KIV10-P, KIV5–10). C, comparison of 17K treatment with point mutants (17KΔV and 17KΔAsp). D, 17K treatment was carried out in the presence of Y27632 (5 μm; cells were pretreated with this compound for 1 h) or ε-ACA (80 mm).