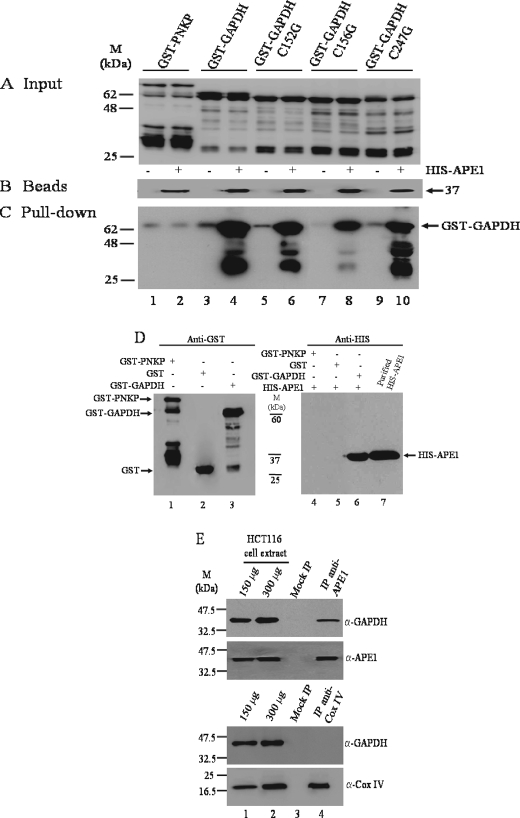
FIGURE 2.
GAPDH interacts with APE1 in vitro and in vivo. A, the indicated GST-tagged input proteins were isolated from E. coli expression system, purified on a GST affinity column, and analyzed by Western blot probed with anti-GST polyclonal antibodies. Lanes 1–10 each contained 200 ng of the purified proteins. B, Talon beads (30 μl each lane) empty (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9) and with bound His-APE1 (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) used for pulling down the GST-tagged proteins in A were probed with anti-His monoclonal antibody. C, the empty Talon beads (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9) or Talon beads with His-APE1 (400 ng) (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) were mixed with the indicated purified GST-tagged proteins (2000 ng each) and washed, and the aliquots (30 μl) were directly assessed for the bound GST-tagged proteins by Western blot probed with anti-GST polyclonal antibodies. D, GST affinity beads containing either purified GST-PNKP (lane 1), GST (lane 2), or GST-GAPDH (lane 3) were mixed with purified His-APE1 (400 ng), washed, and directly assessed for bound His-APE1 (lanes 4–6) by Western blot probed with anti-His monoclonal antibody. Lane 7, purified His-APE1 (150 ng). Molecular mass standards (kDa) are shown in the middle. E, total cell extract (1.5 mg) derived from HCT116 cells was incubated without and with either anti-APE1 or anti-COX IV antibodies and subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by Western blot probed with the indicated antibodies. Lanes 1 and 2, 150 and 300 μg of total cell extracts; lane 3, mocked immunoprecipitation (no antibodies); lane 4, coimmunoprecipitation with either anti-APE1 or anti-COX IV antibodies.