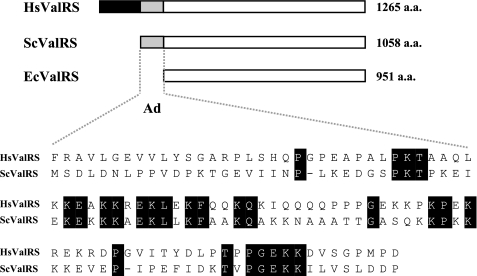
FIGURE 1.
Ads of yeast and human ValRSs. A, comparison of E. coli, yeast, and human ValRSs. Although the catalytic cores of ValRSs from human, yeast, and E. coli are significantly homologous to one another, their N termini vary. The yeast protein contains an N-terminal domain of ∼97 residues, which is absent from its E. coli counterpart, but is conserved in its human homologue. The Ad of human ValRS can be roughly divided into two parts: a hydrophobic portion (residues 1–199) and a positively charged portion (residues 200–298). B, sequence alignment between the Ad of yeast ValRS (residues 1–97) and the positively charged portion of the Ad of human ValRS (residues 200–298). Hs, Homo sapiens; Sc, S. cerevisiae; Ec, E. coli.