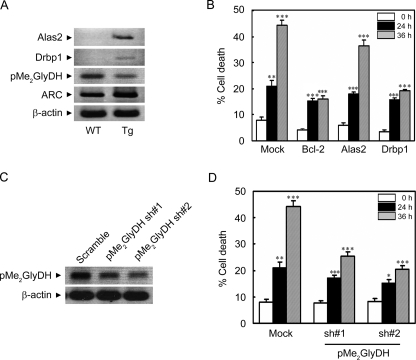
FIGURE 5.
Regulation of ischemic/hypoxic cell death by Drbp1 and pMe2GlyDH. A, RT-PCR analysis showing expressional regulation of Alas2, Drbp1, and pMe2GlyDH in the hearts of ARC Tg mice. Total RNA was isolated from the hearts of 6-week-old WT and ARC Tg mice. RT-PCR analysis was performed using gene-specific synthetic oligonucleotides. β-Actin was used as an internal control. B, suppression of hypoxic death of the primary cardiomyocytes by the ectopic expression of Drbp1. Cardiomyocytes were cultivated from neonatal mice, cotransfected with pGFP, and pcDNA (Mock), pBcl-2, pAlas2, or pDrbp1 for 48 h, and then left untreated or exposed to the hypoxic condition for the indicated times. Determination of cell death was assessed based on the morphology of green fluorescent protein-positive cells under a fluorescence microscope. Bcl-2 was employed as a positive control. Bars represent mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. C and D, reduced expression of pMe2GlyDH protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxic cell death. Neonatal cardiomyocytes were cultured from WT mice, cultivated for 3 days in vitro, and transfected with pMe2GlyDH-shRNA (sh) numbers 1 or 2 for 48 h. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to RT-PCR analysis to examine the expression of pMe2GlyDH (C). After transfection with pMe2GlyDH-shRNA, the cells were left untreated or exposed to the hypoxic condition for 24 or 36 h (D). Cell death were examined as described in B.*, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001; ***, p < 0.0001 versus control.