FIGURE 1.
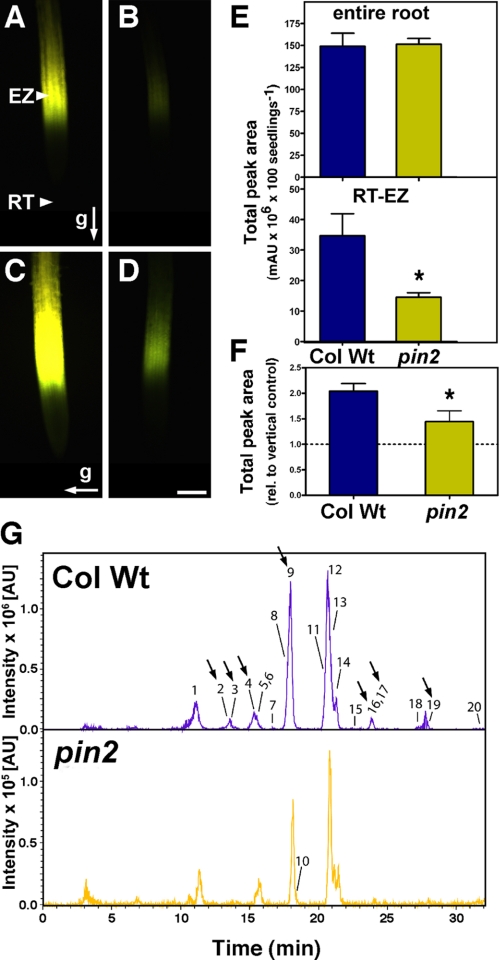
Defects in basipetal auxin transport are associated with altered root flavonoid accumulation. A-D, flavonoid accumulation in the entire root and root elongation zone of wild type (Col Wt; A and C) and pin2 (B and D). Accumulation of flavonoids in control and 2-h gravity-stimulated roots visualized in situ using DPBA (yellow fluorescence) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The arrows indicate the direction of the gravity vector relative to the root. Bar, 100 μm. E, total amount of flavonoid derivatives detected in the entire root and RT-EZ of wild type and pin2. F, gravity-induced root phenolic compound accumulation normalized to phenolic compound accumulation in vertical control. Values represent mean ± S.E. (n = 2-5 replicates); *, significantly different from the wild type (Student's t test, p < 0.05). G, representative sum of extracted ion chromatograms [M - H]- of flavonoid derivatives found in wild type and pin2 RT-EZ analyzed by HPLC-ESI-MS. Significantly altered compounds are indicated by arrows. Peak numbers correspond to flavonoid derivates listed in Table 1. Note the 10 times lower intensity scale for pin2 root elongation zone in comparison to wild type.