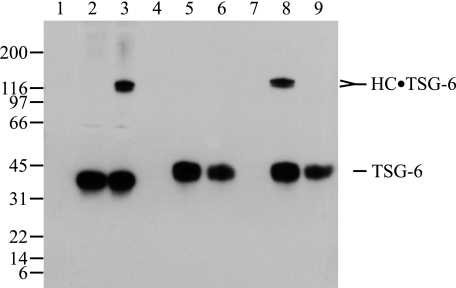
FIGURE 5.
Mutation of Ser28 in TSG-6 prevents covalent complex formation. The complex formation of wild-type and the TSG-6 S28A mutant were analyzed by reduced SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using an anti-TSG-6 antibody. As controls purified IαI and purified wild type TSG-6 expressed in insect cells were analyzed alone (lanes 1 and 2), and following coincubation (lane 3). The medium from cells transfected with an unrelated protein (extracellular superoxide dismutase) was included as a negative control (lane 4). The cell culture medium from mammalian cells transfected with TSG-6 wild type cDNA and TSG-6 S28A mutant cDNA were analyzed alone (lanes 5 and 6). IαI was incubated with medium from mammalian cells transfected with cDNA encoding an unrelated protein (extracellular superoxide dismutase) (lane 7), medium from mammalian cells transfected with TSG-6 wild type cDNA (lane 8), and medium from mammalian cells transfected with the TSG-6 S28A mutant cDNA (lane 9). The immunoblot shows that both wild type and mutant TSG-6 were present in the cell culture medium, but only the wild type TSG-6 formed covalent complexes with IαI. The slightly shorter migration of TSG-6 expressed in mammalian cells compared with TSG-6 expressed in insect cells is most likely caused by differences in glycosylation. The results support that HC·TSG-6 complex formation requires Ser28 of TSG-6 and that no other residues are able to form the cross-link.