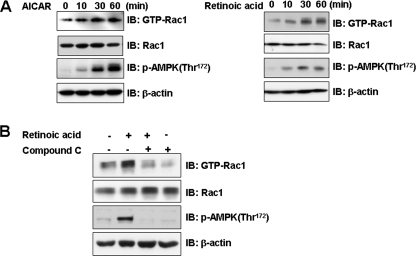
FIGURE 2.
Retinoic acid activates Rac1. A, time-dependent Rac1 activation by retinoic acid and AICAR. C2C12 cells were stimulated for the indicated times with either 10 μm retinoic acid or 1 mm AICAR. The cell lysates were affinity precipitated with GTP-PBD bound to glutathione-agarose beads. Precipitated GTP-Rac1 was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Rac1 antibody. Blotting with anti-phospho-AMPK and Rac1 antibodies was conducted as an experimental control. Blotting with anti-β-actin antibody was conducted as a protein loading control. B, AMPK-dependent Rac1 activation by retinoic acid. C2C12 cells were stimulated with retinoic acid in the presence of compound C (10 μm), a selective inhibitor of AMPK. The cell lysates (20 μg) were affinity precipitated with GTP-PBD bound to glutathione-agarose beads. Precipitated GTP-Rac1 was detected by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-Rac1 antibody. Blotting with anti-phospho-AMPK and Rac1 antibodies was conducted as an experimental control. Blotting with anti-β-actin antibody was conducted as a protein loading control. These results represent one of three independent experiments.