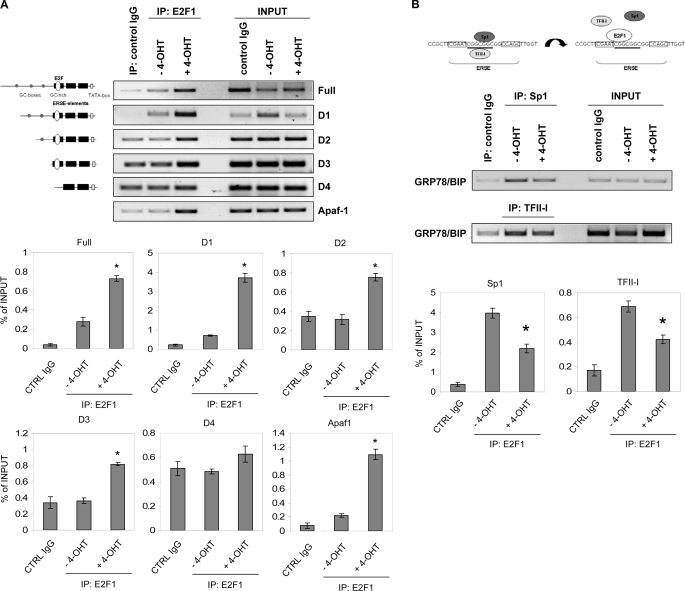
FIGURE 4.
E2F1 binds to the GRP78/BIP promoter in vivo by interfering with ER stress element-binding factors. A, serum-starved Saos-2 cells stably transfected with ER-E2F1 were grown in the presence or absence of 4-OHT for 24 h. Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed using either a control IgG antibody or antibody against E2F1. PCR primers were designed to amplify the different GRP78/BIP promoter fragments spanning from -371 to +2 (full), -304 to +2 (D1), -220 to +2 (D2), -159 to +2 (D3), and -109 to +2 (D4). PCR primers for the Apaf-1 promoter were used as positive control. Input lane, 10% of total chromatin used in chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. B, chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed under the same conditions as in A using specific antibodies against Sp1 or TFII-I. PCR primers were used to amplify the GRP78/BIP promoter fragment between -220 and +2. Representative bands are indicated. Bar graphs show results from two independent experiments as relative software units cleared for background signals and normalized to input bands. Data represent the mean ± S.D. Significant differences in E2F1, Sp1, or TFII-I enrichment of chromatin in 4-OHT-treated versus untreated cells (A, p ≤ 0.005; B, p ≤ 0.01) are labeled with an asterisk (t test).