Abstract
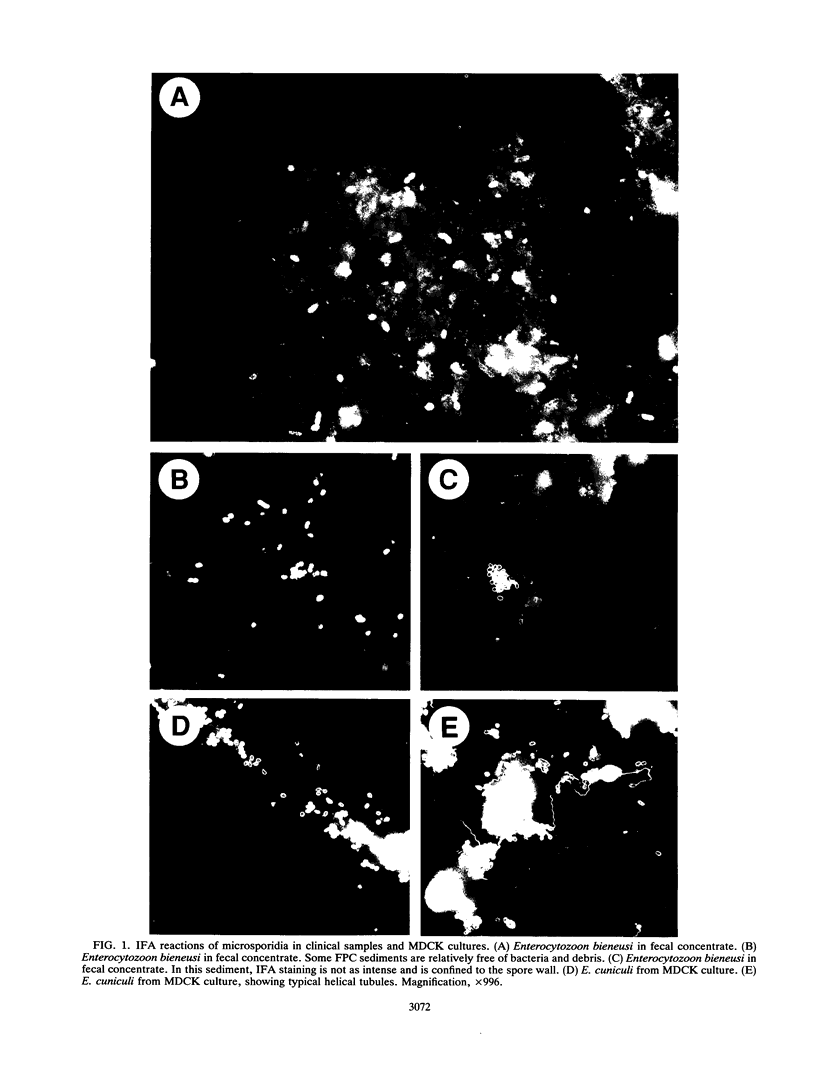
Three polyclonal mouse antisera, to Encephalitozoon cuniculi, Nosema algerae, and Nosema corneum, and two polyclonal rabbit antisera, to E. cuniculi and Encephalitozoon hellem, were used in an indirect fluorescent-antibody assay (IFA) with Enterocytozoon bieneusi, E. cuniculi, and Encephalitgozoon. hellem spores (spores of the last two were taken from culture). Enterocytozoon bieneusi cannot be cultured. By IFA, antisera to E. cuniculi and E. hellem reacted strongly and equally with each other's spores. The mouse antisera reacted strongly with the homologous species, but for these there was segmental and particulate or "dot" staining of heterologous microsporidian spores, indicating cross-reactions with more selected antigens. In fecal samples, cross-reactions with both mouse and rabbit antisera were sometimes seen with different yeast species, with species of streptococci, and species of gram-negative rods. There were no cross-reactions to staphylococci. Enterocytozoon bieneusi was easily identified in duodenal and colonic biopsies, duodenal and colonic fluids, and feces of symptomatic AIDS patients by IFA. In a study of 12 AIDS patients with diarrhea, the new IFA identified microsporidia in all of 11 fecal samples, three colon fluids, six duodenal fluids, and three duodenal biopsy touch preparations. Although the fecal sample of 1 of the 12 was negative, the patient's duodenal fluid contained microsporidian spores by IFA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Canning E. U., Hollister W. S. Microsporidia of mammals--widespread pathogens or opportunistic curiosities? Parasitol Today. 1987 Sep;3(9):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(87)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desportes I., Le Charpentier Y., Galian A., Bernard F., Cochand-Priollet B., Lavergne A., Ravisse P., Modigliani R. Occurrence of a new microsporidan: Enterocytozoon bieneusi n.g., n. sp., in the enterocytes of a human patient with AIDS. J Protozool. 1985 May;32(2):250–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier E. S., Didier P. J., Friedberg D. N., Stenson S. M., Orenstein J. M., Yee R. W., Tio F. O., Davis R. M., Vossbrinck C., Millichamp N. Isolation and characterization of a new human microsporidian, Encephalitozoon hellem (n. sp.), from three AIDS patients with keratoconjunctivitis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):617–621. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck J. A., Greeley E. Microsporidia and human infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):158–165. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]