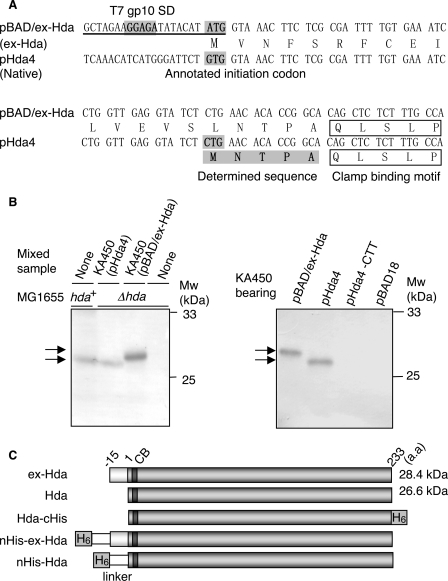
FIGURE 1.
Identification of the Hda initiation codon. A, hda upstream DNA sequences within pBAD/ex-Hda and pHda4. pHda4 carries the chromosome-derived original upstream region. pBAD/ex-Hda carries the modified upstream region (underlined). SD sequence derived from the T7 phage gp10, the positions corresponding to the annotated GUG, and identified CUG initiation codons are shaded. The N-terminal amino acid sequence determined by Edman degradation is also shaded. The clamp-binding motif is indicated. B, Western blot analysis of Hda. KA450 [ΔoriC rnhA dnaA] cells carrying the indicated plasmids were grown, followed by induction of Hda as described under the “Experimental Procedures,” and Western blot analysis was performed (0.013 μl for pBAD/ex-Hda or 2.5μl for pHda4, pHda4-CTT, and pBAD18) (left and right panels). Left panel, MG1655 (hda+) cells and MG1655 derivative MK86 (Δhda) cells were grown at 37 °C in LB medium until the A600 was equal to 0.5; aliquots (80 μl) of the cultures were also used for the indicated lanes with or without mixing with the indicated KA450 sample. As the amount of the KA450 sample was minimal, Hda expressed from the KA450 chromosome was below the detectable level. MK86 was used as a negative control. Also the MK86 sample was mixed with the KA450 samples to normalize the total protein amount. The migration positions of the Hda proteins (arrows) and molecular weight standards (Mw) are indicated. In pHda4-CTT, the CUG initiation codon of Hda was substituted to CUU. pBAD18 was a vector used. C, structures of Hda derivatives used in this study. CB and H6 indicate the clamp-binding motif and hexahistidine tag, respectively. Hda is the same as ntHda.