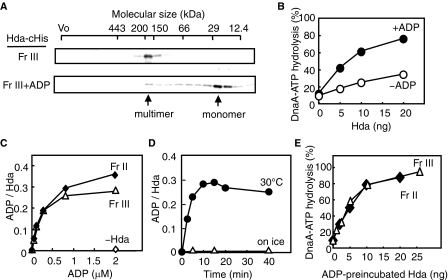
FIGURE 4.
ADP dissociates Hda-cHis multimers to monomers. A, gel filtration analysis. Hda-cHis Fr III (Fr III, 0.5 μg) was analyzed using a Superdex-200 PC 3.2/30 column. Hda-cHis Fr III (0.5 μg) was incubated at 30 °C for 20 min in the presence of 100 μm ADP and analyzed in a similar manner (Fr III+ADP). Eluted proteins were collected in 30-μl fractions, followed by analysis by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. Arrows indicate the peak fractions of Hda-cHis. B, DnaA-ATP hydrolysis activity of Hda-cHis Fr III was analyzed in a staged RIDA reconstituted system in the presence (+ADP) or absence (–ADP) of 30 μm ADP, as described for Fig. 3C. C, ADP binding activities of Hda-cHis Fr II and Hda-cHis Fr III. These fractions were incubated at 30 °C for 20 min in the presence of the indicated concentration of [3H]ADP, before the filter-retention assay was performed. Bound ADP molecules per Hda monomer are presented. D, Hda-cHis Fr III (55 ng or 2 pmol as monomers) was incubated at 30 °C or on ice for the indicated time in the presence of 0.8 μm [3H]ADP, followed by the filter-retention assay. E, Hda-cHis Fr II and Hda-cHis Fr III were incubated at 30 °C for 20 min in the presence of 30 μm ADP, followed by a DnaA-ATP hydrolysis activity assay using a staged RIDA reconstituted system in the presence of the DNA-loaded clamp (20 fmol as clamp), [α-32P]ATP-DnaA (0.5 pmol), and 30 μm ADP.