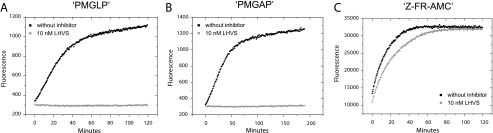
FIGURE 4.
Specific inhibition of CatS prevents digestion of designed substrates by
endosomal fractions; comparison with an unspecific substrate.
Time-progress curves of peptide substrate hydrolysis reactions catalyzed by
macrophages endosomal fractions followed by fluorescence emission. 0.67
μgof total protein from macrophage endosomal fractions were preincubated
for 1 h at 37 °C: ▪, without inhibitor;
 , with 10 nm
LHVS. All of the assays were performed in triplicate at 37 °C in 50
mm sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.5). A, hydrolysis of the
internally quenched fluorescent peptide
Mca-GRWPPMGLPWE-Lys(Dnp)-DArg-NH2 (PMGLP) at a concentration of 20
μm. Progress of product formation was recorded over 2 h by
fluorescence emission of the N-terminal Mca group at 405 nm, following
extinction at 340 nm. LHVS prevents the hydrolysis. B, hydrolysis of
the internally quenched fluorescent peptide
Mca-GRWHPMGAPWE-Lys(Dnp)-DArg-NH2 (PMGAP) at a concentration of 20
μm. Progress of product formation was recorded over 3 h
(λex = 340 nm, λem = 405 nm). LHVS
prevents the hydrolysis. C, hydrolysis of the unspecific fluorogenic
peptide Z-FR-AMC at a concentration of 100μm. Progress of
product formation was recorded over 2 h by fluorescence emission of the AMC
group (λex = 360 nm, λem = 465 nm). LHVS
reduces the initial velocity of the hydrolysis reaction but does not prevent
it.
, with 10 nm
LHVS. All of the assays were performed in triplicate at 37 °C in 50
mm sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.5). A, hydrolysis of the
internally quenched fluorescent peptide
Mca-GRWPPMGLPWE-Lys(Dnp)-DArg-NH2 (PMGLP) at a concentration of 20
μm. Progress of product formation was recorded over 2 h by
fluorescence emission of the N-terminal Mca group at 405 nm, following
extinction at 340 nm. LHVS prevents the hydrolysis. B, hydrolysis of
the internally quenched fluorescent peptide
Mca-GRWHPMGAPWE-Lys(Dnp)-DArg-NH2 (PMGAP) at a concentration of 20
μm. Progress of product formation was recorded over 3 h
(λex = 340 nm, λem = 405 nm). LHVS
prevents the hydrolysis. C, hydrolysis of the unspecific fluorogenic
peptide Z-FR-AMC at a concentration of 100μm. Progress of
product formation was recorded over 2 h by fluorescence emission of the AMC
group (λex = 360 nm, λem = 465 nm). LHVS
reduces the initial velocity of the hydrolysis reaction but does not prevent
it.