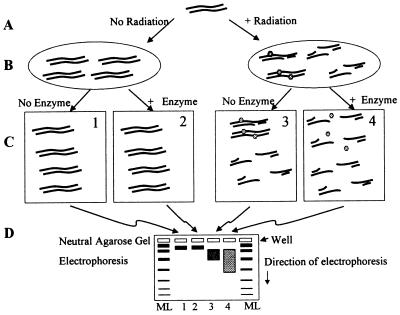
Figure 1.
Determination of clustered lesions. (A) DNA remains unirradiated (Left) or is exposed to ionizing radiation (Right). (B) Unirradiated DNA is unchanged in size (left oval), whereas radiation produces DSBs and clustered lesions containing damaged bases or abasic sites at approximately equal frequencies (right oval). (C) Treatment of unirradiated DNA with a lesion-specific enzyme has little or no effect on the size of the DNA molecules (block 2 relative to block 1). Irradiated DNA contains both DSBs (which reduce the size of the DNA) and clustered lesions (which do not reduce DNA size) (block 3); however, lesion-specific enzyme treatment of irradiated DNA (through release of damaged bases and AP endonuclease action) generates de novo DSBs at cluster sites (block 4). (D) DNA molecules from experimental samples, along with molecular length standard DNAs (ML), are dispersed according to double-strand molecular length by agarose gel electrophoresis under neutral conditions. Ionizing radiation also produces isolated DNA damages (not shown) that lesion-specific enzyme treatment converts to SSBs but not to DSBs.