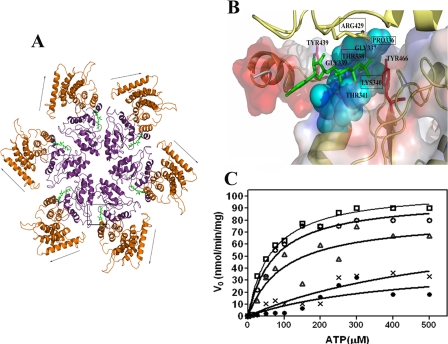
FIGURE 5.
In silico modeling and mutational analysis of Rv3868. A, hexameric association in Rv3868. The nucleotide binding sites occur at the intersubunit interfaces as in other AAA-ATPases. The arrows indicate movement of the N-terminal domain predicted by the dynamic quenching and other experiments. The ATP-binding site is marked by a box. B, close-up of the ATP binding site in Rv3868. The residues corresponding to the Walker A motifs are indicated by cyan space-filled models. Two tyrosine residues (positions 439 and 466) in the close vicinity of the nucleotide are depicted as red sticks. Arg-429, the predicted sensor arginine from the modeling studies, is depicted as a yellow stick and is from a neighboring subunit. C, Michaelis-Menten plots of ATP hydrolysis by CT-Rv3868 (□) and CT-Rv3868P336A (○), CT-Rv3868T338A (•), CT-Rv3868K340A (▵), and CT-Rv3868R429A (*).