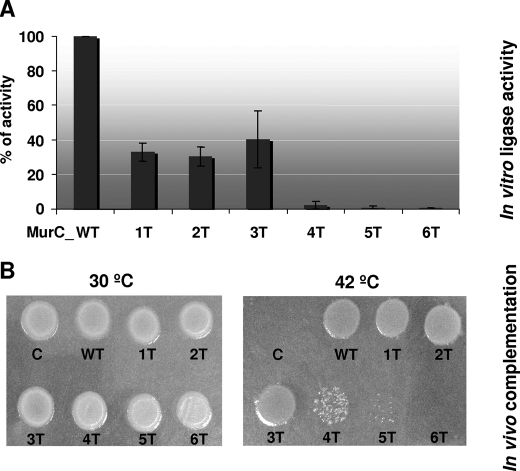
FIGURE 6.
Effect of MurC phosphorylation site mutagenesis on in vitro and in vivo activity. A, in vitro assays of the wild-type and phosphorylation site mutant (1T to 6T) MurC proteins. Purified MurC proteins were assayed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Three independent experiments were performed, yielding similar results. The activity of the wild-type protein (here represented as 100%) was 2650 nmol/min/mg of protein, and those of the 1T, 2T, 3T, 4T, 5T, and 6T MurC mutants were 875, 800, 1050, 75, 20, and 10 nmol/min/mg of protein, respectively. B, in vivo functional complementation assays using an E. coli temperature-sensitive murC mutant strain. The pTrc99A plasmid vector and derivative plasmids expressing wild-type or mutated versions of the C. glutamicum MurC protein were transformed into the E. coli thermosensitive murC mutant strain H1119. Functional complementation was assayed by following the growth of the transformants at the permissive temperature of 30 °C (left panel), or at the non-permissive temperature of 42 °C (right panel).