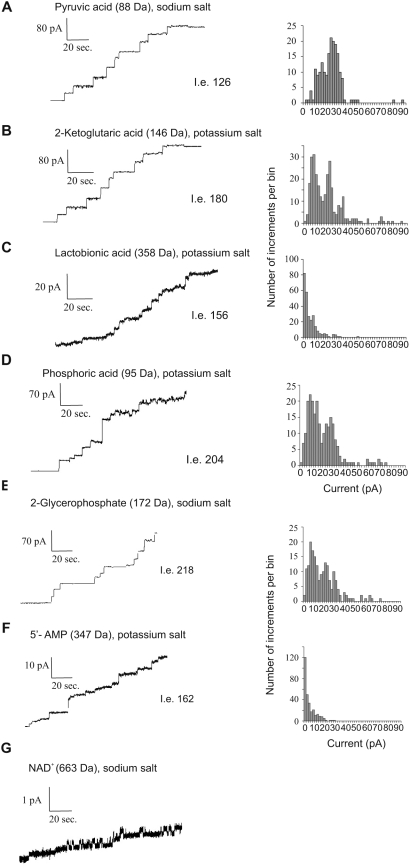
Figure 5. Multiple-channel recording of purified Pxmp2 using different organic anions as electrolytes.
The measurements were made using as a bath 1.0 M solutions of potassium or sodium salts of the anions at pH 7.2. The pH of solutions was adjusted by corresponding sodium or potassium hydroxides. The solutions were buffered with 10 mM MOPS, pH 7.2. Phosphate was used as 1 M potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.2. Molecular masses of the corresponding anions are shown in brackets. The total number of insertion events (I.e.) is also shown. Two different batches of purified Pxmp2 were used with similar results obtained; typical pictures are presented. The purified Pxmp2 channel was also active with glycolic, lactic, acetic and allantoic acids (data not shown). We did not analyze in depth the dependence between size of anions and their conductance level since the hydrated radii of most of these anions are not known. However, as can be seen from the data, the conductivity of the Pxmp2 channel is clearly dependent on the size of the anions if their molecular mass exceeds 300 Da (compare, e.g., panels A and B with panels C and F), indicating partial restriction in the diffusion of these anions through the channel.