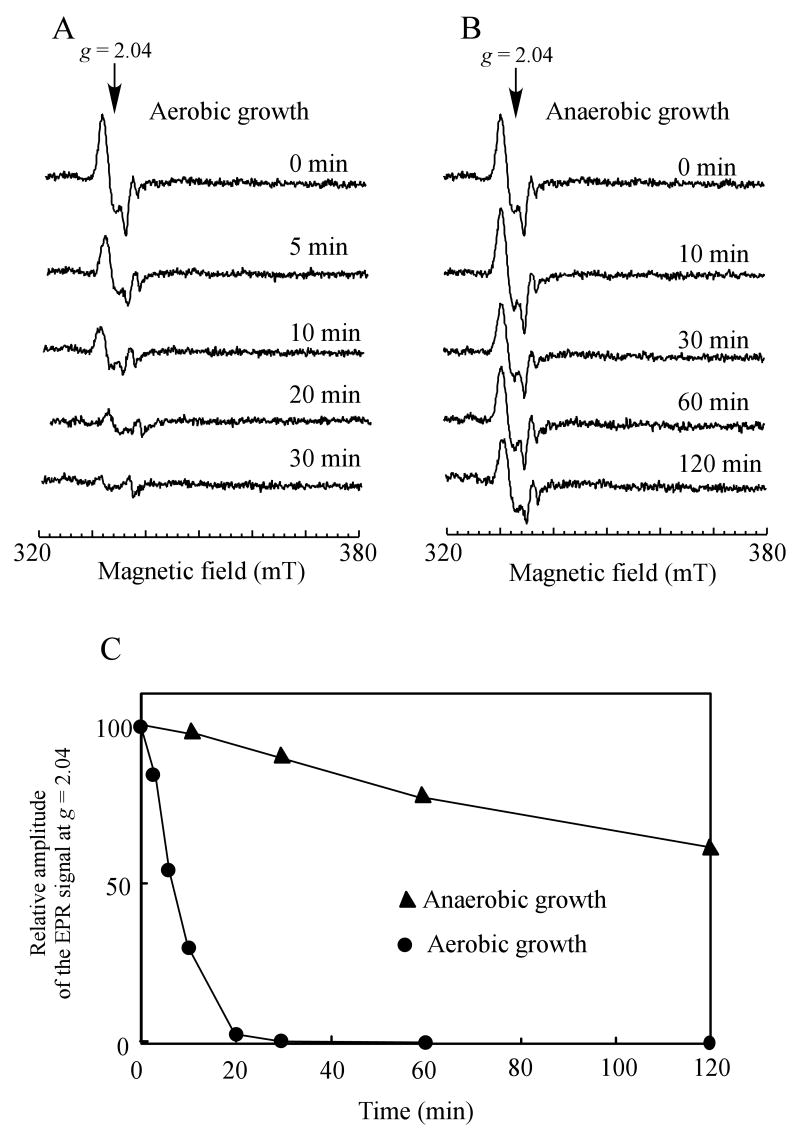
Figure 5. Aerobically growing E. coli cells have a robust repair activity for the protein-bound DNICs.
Exponentially growing E. coli cells (concentrated to O.D. at 600 nm of 5.0) were exposed to pure NO gas at a rate of 100 nM per second for 10 min using the Silastic tubing NO delivery system anaerobically, followed by purge with pure argon gas. The NO-exposed cells were then returned to either aerobic or anaerobic growth conditions in minimal medium containing 0.2% glucose. A), the EPR spectra of the NO-exposed E. coli cells at indicated time after returned to aerobic growth conditions. B), the EPR spectra of the NO-exposed E. coli cells at indicated time after returned to anaerobic growth conditions. C), decay kinetics of the EPR signal at g = 2.04 of the NO-exposed E. coli cells under aerobic (closed circles) and anaerobic (closed triangles) growth conditions.